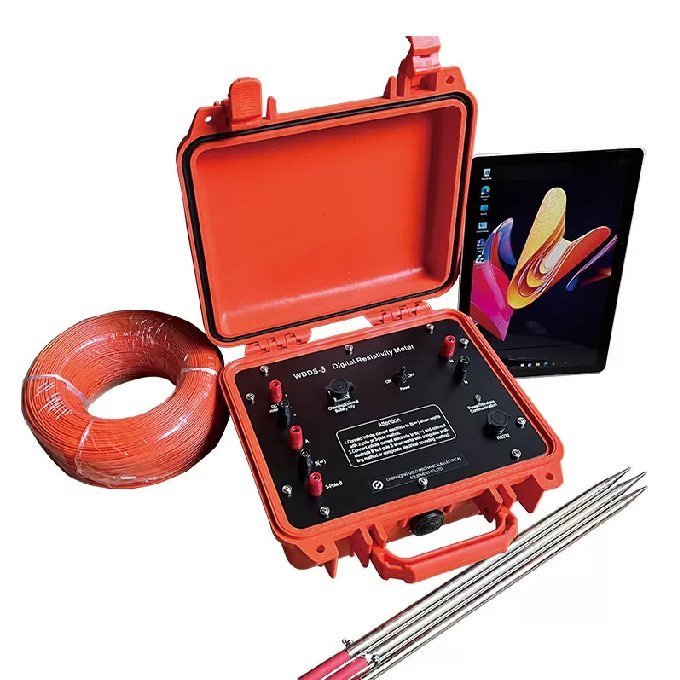
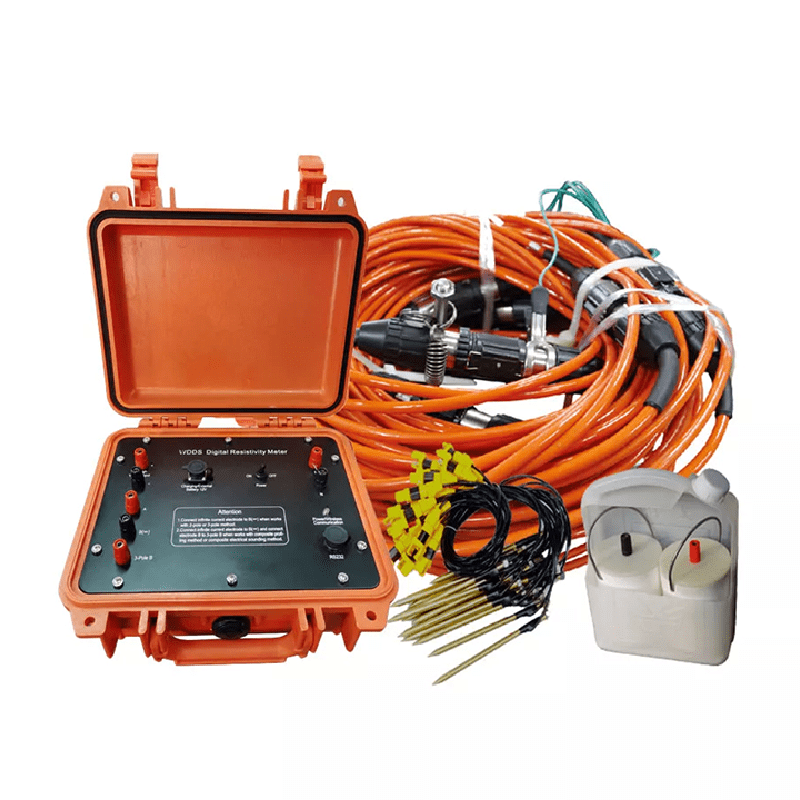
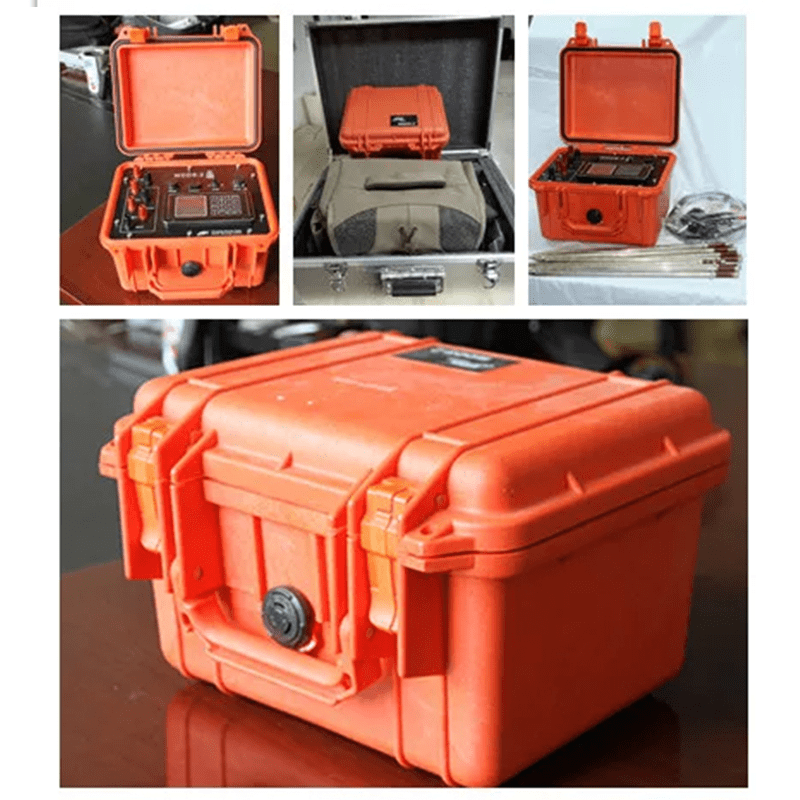
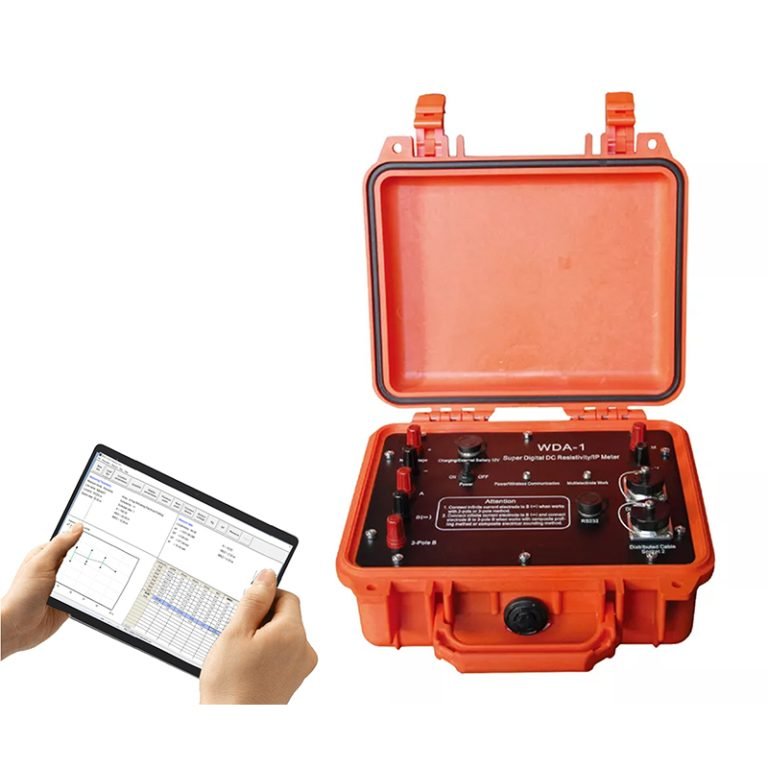
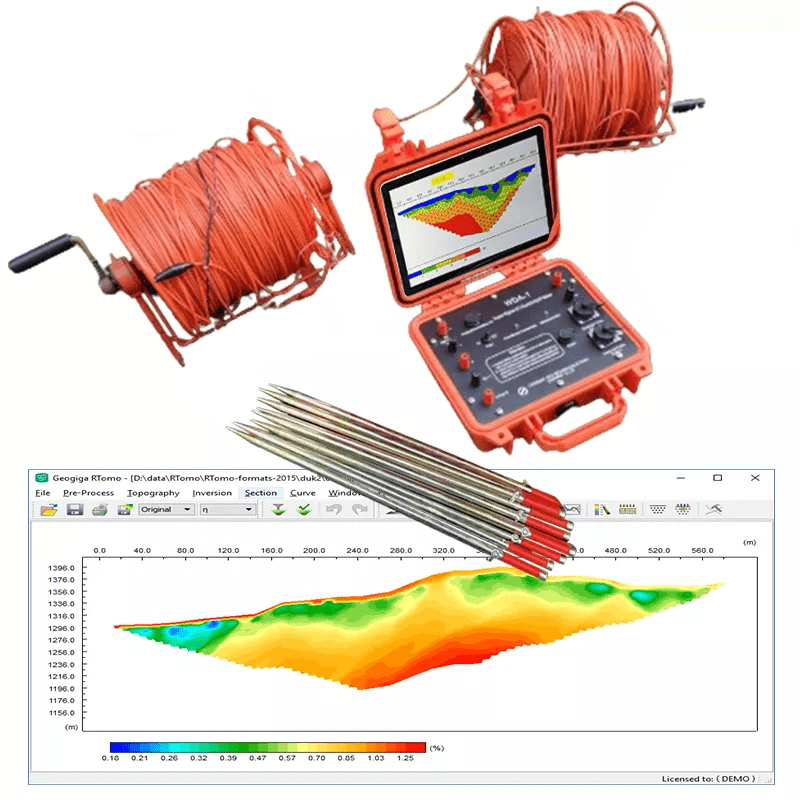
Welcome to Geotech!

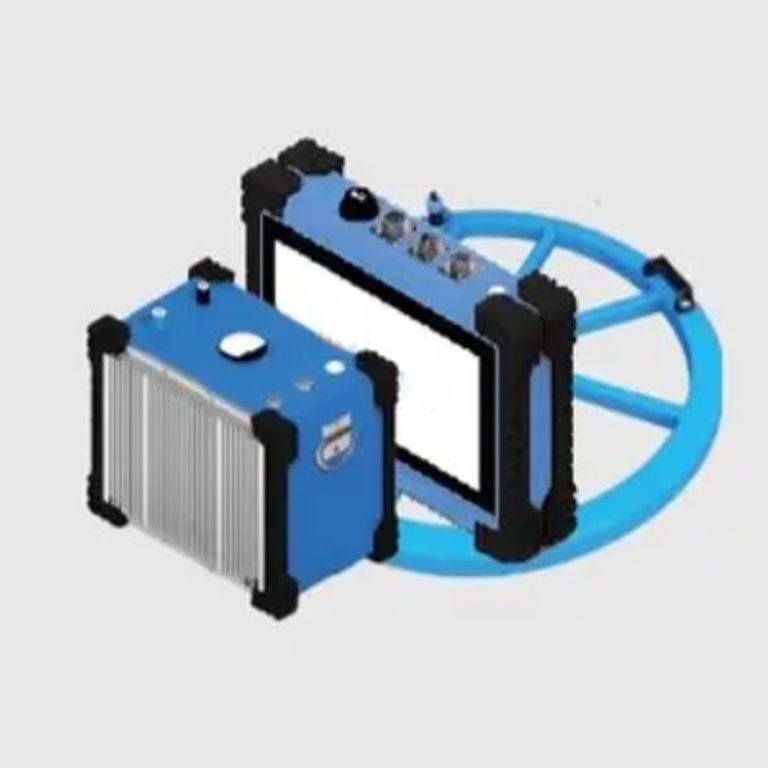
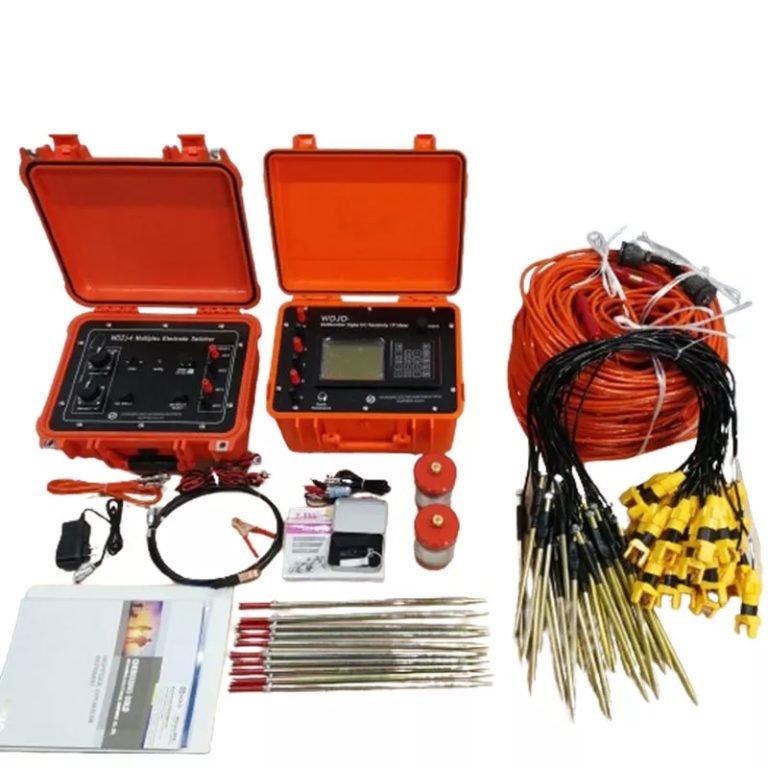
WDDS-3C Digital Resistivity Meter
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
- Tuursmitter and receiver designed in one unit.
- Large power up to 6000W, 50V wide voltage input range.
- Automatic compensation of self-potential, drift and electrode polarization .
- Monitoring the dynamic variation of MN electrode potential through inspecting its ground resistance.
- Receiver supports transient over-voltage protection; transmitter supports overvoltage, over-current and AB open-circuit protections.
- Internal 12V lithum battery for 20 hours contiously work.
- Communicated by USB port.
- Store measuring data for more than 150,000 times.
- Measuring data includs voltage, current, resistivity, relative error, SP, array constant, measuring point and so on.
Description
 Abstract
Abstract
The WDDS-3C digital resistivity meter is an advanced DC resistivity equipment. It incorporates 32-bit microcontroller technology and 24-bit A/D technology, making it a cutting-edge solution for resistivity surveys. This versatile instrument is suitable for various applications including mineral resource detection, geophysical exploration in urban areas, railway and bridge inspections, hydrology, engineering geology, and geothermal prospecting. It enables precise detection of metal and nonmetal resources, groundwater exploration, fault identification in dam bases and flood protection levees, and more.

 Working principle
Working principle
The electrical resistivity method is an active geophysical technique. It employs an artificial source which is introduced into the ground though a pair of electrodes. The procedure involves measurement of potential difference between other two electrodes in the vicinity of current flow. Apparent resistivity is calculated by using the potential difference for the interpretation. These electrodes by which current is introduced into the ground are called Current electrodes and electrodes between which the potential difference is measured are called Potential electrodes.
 Applications
Applications
● Metal and nonmetal mineral resources detection
● City geophysical exploration, railway and bridge inspection and so on
● Hydrology and engineering geology as seeking for ground water, inspecting dam base and flood protection levee for incipient faults
● Geothermal prospecting
 Features
Features
● Tuursmitter and receiver designed in one unit.
● Large power up to 6000W, 50V wide voltage input range.
● Automatic compensation of self-potential, drift and electrode polarization .
● Monitoring the dynamic variation of MN electrode potential through inspecting its ground resistance.
● Receiver supports transient over-voltage protection; transmitter supports overvoltage, over-current and AB open-circuit protections.
● Internal 12V lithum battery for 20 hours contiously work.
● Communicated by USB port.
● Store measuring data for more than 150,000 times.
● Measuring data includs voltage, current, resistivity, relative error, SP, array constant, measuring point and so on.
 Specifications
Specifications
Receiving section
| Item | Parameters |
| Voltage channel | ±50V, ±0.2% ±1LSB, 24-bit A/D |
| Maximum sampling resolution of voltage | 0.01μV |
| Input impedance | ≥50MΩ |
| SP compensation range | ±10V |
| Current channel | 5A, ±0.2% ±1LSB, 24-bit A/D |
| Maximum sampling resolution of current | 0.02μA |
| Suppression | ≥80dB for 50Hz industrial frequency (common mode interference or differential mode interference) |
Transmitter
| Item | Parameters |
| Transmit power | 6000W |
| Power supply voltage | ±1200V (2400Vp-p) |
| Power supply current | ±5A (7Ap-p) |
| Power supply pulse waveform | Duty cycle is 1:1, bipolar |
Other parameters
| Item | Parameters |
| Instrument power source | Built-in 7.4V and 48V lithium battery (or external 12V power supply) |
| Mainframe interface | A, B, M, N, DC high voltage, external battery, charger, Bluetooth, and USB |
| Built-in high-voltage power supply | Max current: 300mA, voltage options: 50V, 100V, 150V, 200V |
| Working temperature | -10℃ ~ +50℃, 95% RH |
| Storage temperature | -20℃ ~ +60℃ |
| Weight | ≤5.7 Kg |
| Dimensions (L×W×H) | 350mm x 270mm x 200mm |
 Case Study
Case Study
Electrical Resistivity Imaging Method for Evaluate Estuarine Impace on Groundwater Salinization in Pondicherry Coastal Aquifers



FAQ
① In SI, it is m·s-2, and one percent of it is the international unit abbreviation g.u.;
② Conversion between SI and CGS: 1g.u.=10-1 mGal
Gravitational field: The space around the earth with gravity is called the gravitational field.
Gravitational potential: The gravitational potential W in the gravitational field is equal to the work done by a particle of unit mass moving from infinity to that point.
① The normal gravity field of the earth: Assuming that the earth is a rotating ellipsoid (reference plane), the surface is glossy, the internal density is uniform, or it is distributed in concentric layers, the density of each layer is uniform, and the deviation of the shape of the ellipsoid from the geoid is very small, then the gravity field generated by the earth is the normal gravity field.
② The normal gravity value is only related to the latitude, the smallest at the equator and the largest at the poles, with a difference of about 50,000 g.u.; the rate of change of the normal gravity value with latitude is the largest at 45° latitude, and zero at the equator and the poles; the normal gravity value decreases with increasing altitude, and its rate of change is -3.086 g.u.. The main feature of the long-term change is the "westward drift" of the geomagnetic elements, both the dipole field and the non-dipole field drift westward, and have a global nature.
The gravitational field strength is equal to the gravitational acceleration in both numerical and dimensional terms, and the two are in the same direction. In gravity exploration, all references to gravity refer to gravitational acceleration. The gravitational field strength at a point in space is equal to the gravitational acceleration at that point.
Gravity exploration is an exploration method that is based on the density difference of rocks and ores. Since density difference will cause local changes in the normal gravity field of the earth (i.e. gravity anomaly), it is used to solve geological problems by observing and studying gravity anomalies.
-1.png)