Welcome to Geotech!

Decoding Geotech’s Quality Standards for High-Precision Proton Magnetometers
Introduction
In the field of geomagnetic exploration, precision and reliability are paramount. Geotech Instrument Co., Ltd. has established rigorous quality standards to ensure the high-precision performance of its JPMG Proton Magnetometer. This article delves into the technical specifications, field methodologies, and quality assurance protocols that make the JPMG Series a leading choice for geological surveys in extreme environments.

Magnetic Measurement Work Content
According to the Technical Regulations for High-Precision Ground Magnetic Survey, the work content involves conducting 1:10,000 high-precision magnetic surveys over 13.91 km² and 1:5000 high-precision magnetic profile measurements with a point distance of 20 meters. These measurements are crucial for identifying magnetic anomalies associated with mineral deposits and geological structures.
Instruments and Equipment Accuracy Requirements
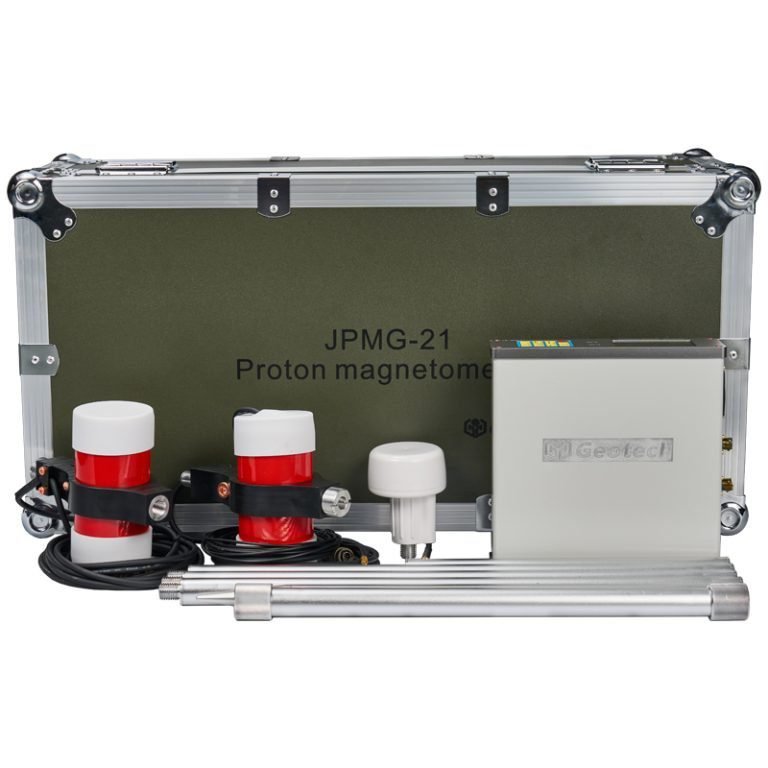
The JPMG Proton Magnetometer is the instrument of choice for high-precision magnetic measurements. It measures the total magnetic field intensity (ΔT) with a total accuracy of 5nT. The magnetometer’s noise error is kept below 2.0nT, ensuring reliable detection of weak magnetic anomalies above 13nT.
Field Work Methods and Techniques
Instrument Calibration and Testing
Before commencing fieldwork, the JPMG Proton Magnetometer undergoes comprehensive performance testing, including noise tests, probe tests, and consistency tests. These tests ensure the instrument meets the required accuracy standards before deployment.
Base Point Layout and Diurnal Variation Monitoring
A magnetic survey total base point is established to serve as the zero point for the entire survey area. Sub-base points are also set up to form a network, ensuring all observations are normalized to the same time through diurnal variation correction.
Field Observation Techniques
Observers use the JPMG Proton Magnetometer to conduct total field observations, starting and ending each closed observation unit at a calibration point. Strict protocols are followed to avoid magnetic interference and ensure data integrity.
Data Management and Quality Inspection
Field data is transferred to a computer daily for 100% self-inspection and acceptance. Data undergoes various corrections, including base point, normal field, diurnal variation, and altitude adjustments. Quality inspections are performed using the “same but three different” principle to ensure accuracy.
Physical Property Work
Physical property measurements are fundamental to geophysical exploration. The JPMG Proton Magnetometer is used to measure the magnetization (K) and residual magnetization (Jr) of rock samples, ensuring data accuracy through repeat measurements and quality checks.
Indoor Data Processing
After field data collection, indoor processing involves applying various corrections using the IGRF 2005 model coefficients. Staff compile and draw maps to guide further fieldwork, ensuring all technical requirements are met.
Conclusion
The JPMG Proton Magnetometer, adhering to Geotech’s stringent quality standards, delivers precise and reliable magnetic measurements. Its robust design and advanced features make it ideal for challenging geological surveys, providing professionals with a powerful tool for mineral exploration and geological research.
-1.png)