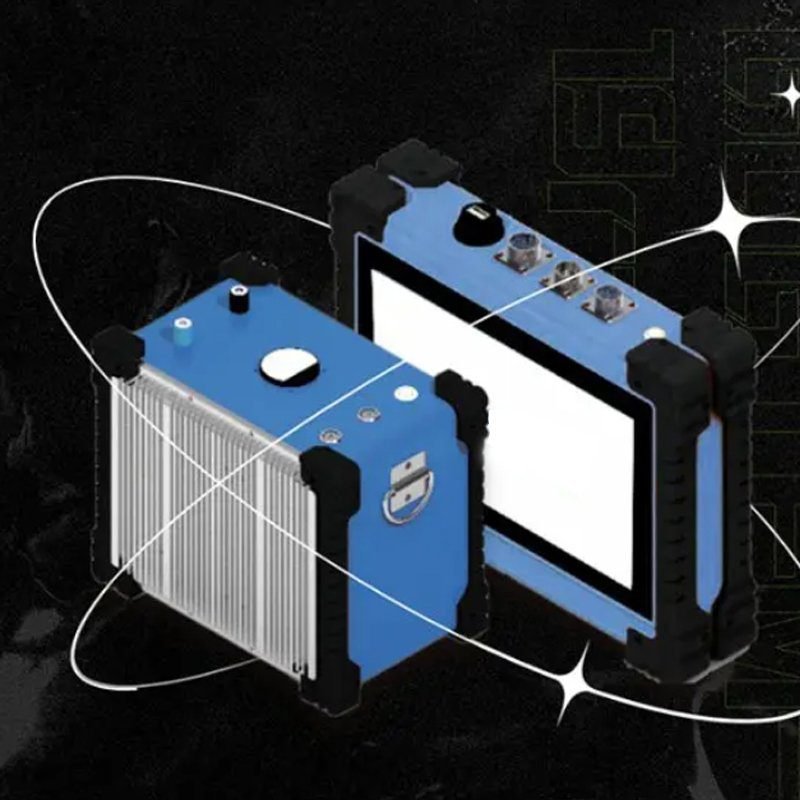
Welcome to Geotech!

GEOTEM-19Rad: Ultra-shallow TEM Instrument for Dual-depth Geological Detection
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
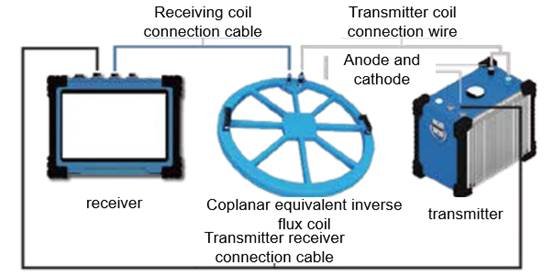
- Technological Breakthrough:Coplanar equivalent inverse flux technology eliminates detection blind zones, with sampling time advanced to 0.1ms for precise 1m ultra-shallow detection.
- Dual-depth Capability:Combines ultra-shallow (1m) and deep (150m) exploration, adapting to diverse geological survey needs.
- High-performance Specs:32-bit AD converter, 160dB dynamic range, 2.24GHz quad-core processor, achieving 0.1% measurement accuracy.
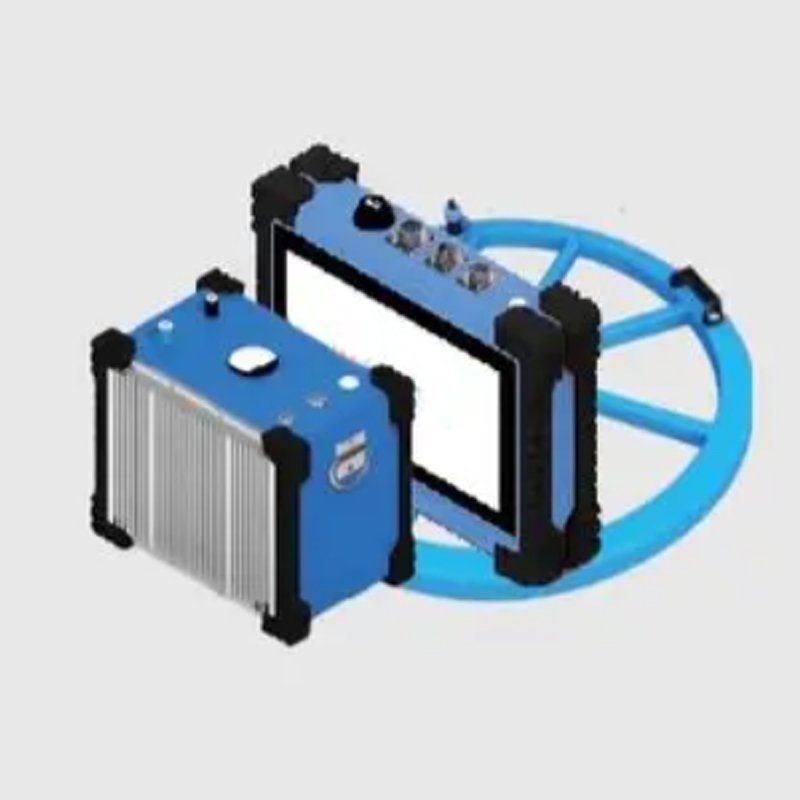
- Portability & Intelligence:10kg lightweight receiver with touchscreen operation and one-key mapping, supported by 8+ hours battery life.
- Anti-interference Strength:Multi-layer anti-interference algorithms ensure precise target positioning in strong interference environments like steel frame bridges.
- Full-scene Application:Covers engineering geological inspection, metal mineral exploration, archaeological research, disaster relief, and other fields.
Description
Ⅰ. Oversea
The GEOTEM-19Rad Ultra-shallow Transient Electromagnetic (TEM) system integrates the Coplanar Equivalent Inverse Flux Principle with Geotech’s extensive industrial experience in transient electromagnetics. It effectively overcomes the inherent detection blind zone of conventional TEM methods, enabling precise ultra-shallow exploration (down to 1-meter depth). Meanwhile, it employs a large-scale central loop configuration for deep exploration, combining ultra-shallow and deep-detection capabilities in a single instrument. This eliminates the need for multiple devices and repeated deployments, significantly enhancing operational efficiency in applications like tunneling, infrastructure safety assessments, and environmental monitoring.
Ⅱ.Principle and advantages



Principle and advantages of coplanar equivalent inverse flux:
- By compensating the reverse power supply current of the transmitting coil, the positive and negative transmitting coils offset the primary field after shutdown, forming a primary field zero-flux region inside the receiving coil. This eliminates the “blind zone” and enables ultra-shallow detection.
- The whole system is processed with high-strength non-metallic materials, making the primary field in the receiving coil cancel each other in positive and negative directions without on-site adjustment in the working area.
- The new “Compensated Transient Electromagnetic Meter” basically eliminates the “turn-off delay” effect of the power supply line, advancing the effective sampling time to 0.1ms and the minimum detection depth to the “meter level.
- Using different sizes of working devices adapts to measurement conditions at different depths, saving working time without field adjustment.
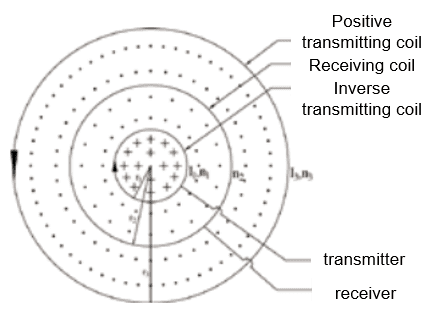
Principle diagram of coplanar equal value reverse flux
Causes of Transient Electromagnetic Detection Blind Zone:
The basic principle of the transient electromagnetic method is to use an ungrounded loop (coil) to send a pulsed electric field to the measured geological body as a field source (primary field) to stimulate the geological body to generate a secondary field. During the gap between emitted pulses, the receiving loop (coil) is used to receive the time-varying response of the secondary field. The position of the abnormal conductor in the geological body is analyzed from the received secondary field information to achieve the purpose of solving geological problems.
However, for the traditional transient electromagnetic method, since the current cannot “return to zero” instantly after shutdown, the induced electromotive force generated by the receiving coil itself is superimposed on that generated by the underground eddy current field in a short period after shutdown. This distorts the early signal of transient electromagnetic measurement, forming a shallow detection “blind zone”.
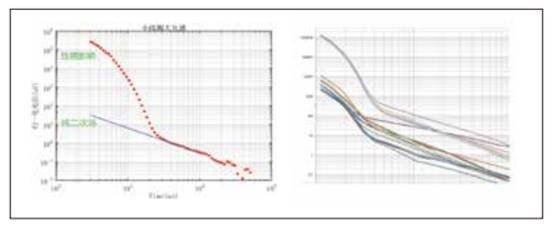
Ⅲ. Features
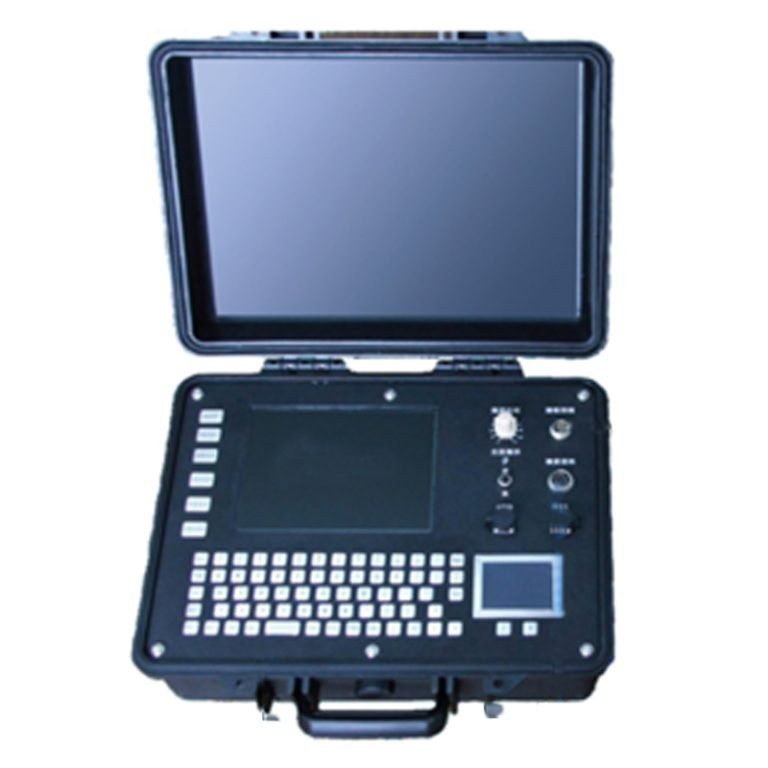
- Portable and Lightweight: The receiver adopts a lightweight metal flat plate design, easy to carry, with touch screen operation, strong and waterproof.
- Integrated Coplanar Equivalent Inverse Flux Coil: Easy to operate, with deep-detection capability and no blind zone.
- High Performance and Low Power Consumption: 2.24GHz quad-core processor, 32-bit AD conversion chip, no operation delay, high measurement accuracy, and wide dynamic range.
- Self-developed Technology Breakthrough: Overcomes the inherent “blind zone” of transient electromagnetics, enabling effective ultra-shallow detection and precise measurement of the shallow part up to 1 meter.
- Intelligent Interpretation System: Full-space interpretation software adapts to underground (roadway, tunnel, etc.) operations, with friendly operation supporting one-key filtering and mapping.
- Universal Compatibility: The universal transient electromagnetic receiver can be equipped with different transmitters and coils to meet the needs of transient electromagnetic detection in explosion-proof environments (coal mines), tunnel advance prediction, and ground surveys.
- Real-time Data Interconnection: Connectable to the advanced detection data online processing and interpretation system to realize real-time upload, storage, interpretation, and mapping of geophysical data.

Ⅳ. Application
Engineering inspection
- Detect geological diseases such as caverns, fractures, karst, and weak layers in the subgrade of highways, airport runways, urban roads, and railway/highway tunnels.
- Detect safety hazards like leakage, voids, and ant nests in the foundation and body of dams (reservoirs, barrage dams, tailings dams, etc.).
Engineering investigation
- Detect shallow karst and evaluate its scale, morphology, and water content.
- Determine the scale, occurrence, and water content of shallow fracture zones.
- Detect 3D characteristics of shallow goafs (distribution range, burial depth, occurrence state, etc.).
- Permafrost exploration: measure thickness, burial depth, and other occurrence characteristics.
Metal Ore Prospecting
- Quickly evaluate the prospect of metal ore rights and explore the scope and occurrence of metal ore bodies.
Archaeological research
- Detect the distribution range and burial depth of ancient tombs in archaeological research.
- Explore metal artifacts in ancient tombs during archaeological studies.
Ⅴ. Technical Parameters
Receiver specifications
| Item | Specifications |
| A/D converter | 32Bit |
| Dynamic range | 160dB |
| Sampling rate | 1μs、4μs、16μs、 |
| Acquisition channel number | 2 |
| Background noise | 1μV |
| Voltage measuring range | -200V-200V |
| Voltage measurement resolution | ≤300nV |
| Measurement accuracy | 0.1% |
| Input gain range | 1/80-8000 |
| Minimum sampling interval | 4μs |
| Noise suppression | >100dB |
| Transmission band | 0-500kHz |
| Stacking number | 1-65535 times |
| Computer system | PC104 Industrial computer, 8.4 “color LCD screen (full Windows interface) |
| Data storage | 2G(expandable) |
| Storage capacity | ≥30000 |
| Data transmission | USB2.0 |
| Power supply | Internal battery work more than 8 hours, external 9-18VDC |
| dimension | 403mm×330mm×178mm |
| weight | 10kg |
| Operating temperature | -10℃-50℃ |
Transmitter technical specifications
| Item | Specifications |
| Transmitting voltag(V) | 36-57 |
| Current intensity(A) | 25、50、100、200 |
| Current pulse width(ms) | 10、20、40 |
| Transmitting waveform | Bipolar square wave with a duty cycle of 1:1 |
| Maximum power(KW) | 12 |
| Synchronous mode | Cable synchronization |
| Turn-off time | It varies with the size of the supply current and the sending coil,0.5-300μs |
| Operating temperature | -10℃-50℃ |
Coil model
| Specification | Detection depth |
| Coplanar equivalent antimagnetic flux | 150m |
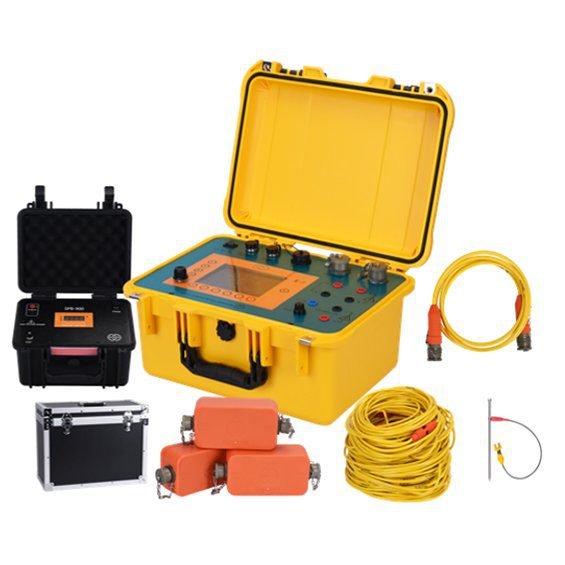
Ⅵ. Configuration
| NO. | Unit | Name | Quantity |
| 1 | Equipment | Transient electromagnetic receiver | 1 set |
| 2 | Attachment | Host charger | 1 set |
| 3 | Main engine transport box | 1 set | |
| Tablet computer | 1 unit | ||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | Tablet charger | 1 set | |
| 6 | Connecting line | 1 set | |
| 7 | Coplanar equivalent anti-flux coil | 1 set | |
| 8 | Air transport box | 1 set | |
| 9 | Software | Interpretive system | 1 set |
Ⅶ. Cases
Cases1:Harbin Civil Air Defense Pipeline Detection
- Location: Harbin
- Burial Depth: 8m
- Content: Detection of 0.6m diameter concrete water pipes in civil air defense projects
- Result: The detection result fully matches the actual situation. The water pipe position can still be detected in the strong interference environment of steel frame bridges, where other methods show poor effects.

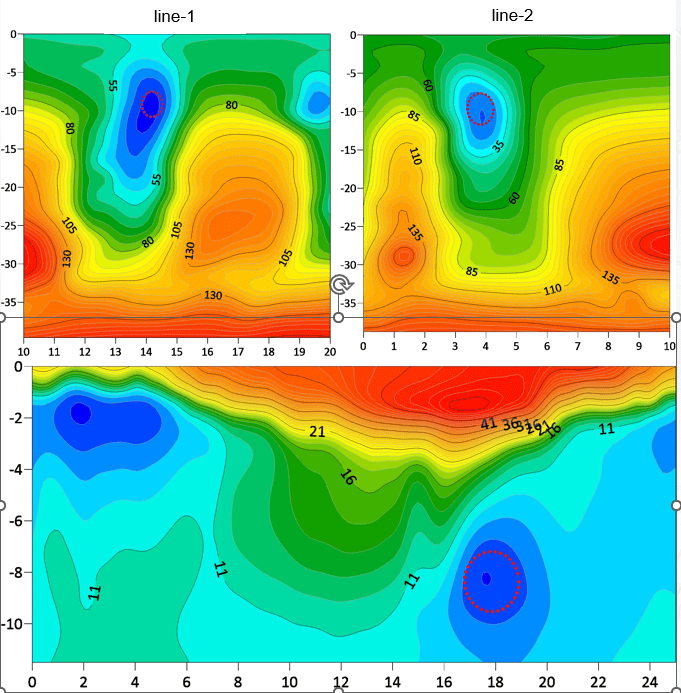
Cases2:Dongting Lake Disaster Relief Detection
- Location: Dongting Lake, Hunan
- Content: Detection of leakage channels during disaster relief, with clear and significant leakage channel indication.
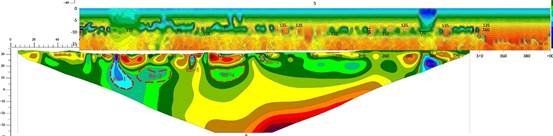


Cases3:Liuzhou Railway Tunnel Survey
- Location: Liuzhou, Guangxi
- Content: Survey of Liuwu Railway Tunnel
- Result: One fault, one structural fracture zone, and two rock mass fracture zones were delineated, which were verified by drilling to be consistent with the actual situation.

FAQ
① In SI, it is m·s-2, and one percent of it is the international unit abbreviation g.u.;
② Conversion between SI and CGS: 1g.u.=10-1 mGal
Gravitational field: The space around the earth with gravity is called the gravitational field.
Gravitational potential: The gravitational potential W in the gravitational field is equal to the work done by a particle of unit mass moving from infinity to that point.
① The normal gravity field of the earth: Assuming that the earth is a rotating ellipsoid (reference plane), the surface is glossy, the internal density is uniform, or it is distributed in concentric layers, the density of each layer is uniform, and the deviation of the shape of the ellipsoid from the geoid is very small, then the gravity field generated by the earth is the normal gravity field.
② The normal gravity value is only related to the latitude, the smallest at the equator and the largest at the poles, with a difference of about 50,000 g.u.; the rate of change of the normal gravity value with latitude is the largest at 45° latitude, and zero at the equator and the poles; the normal gravity value decreases with increasing altitude, and its rate of change is -3.086 g.u.. The main feature of the long-term change is the "westward drift" of the geomagnetic elements, both the dipole field and the non-dipole field drift westward, and have a global nature.
The gravitational field strength is equal to the gravitational acceleration in both numerical and dimensional terms, and the two are in the same direction. In gravity exploration, all references to gravity refer to gravitational acceleration. The gravitational field strength at a point in space is equal to the gravitational acceleration at that point.
Gravity exploration is an exploration method that is based on the density difference of rocks and ores. Since density difference will cause local changes in the normal gravity field of the earth (i.e. gravity anomaly), it is used to solve geological problems by observing and studying gravity anomalies.
-1.png)