Welcome to Geotech!

【WGMD-4】Application of Leachate Distribution and Liner Detection at a Landfill
- Cases, Landfill lnvestigation Cases
- 21 views
Description
Ⅰ.Introduction
Landfills play a critical role in waste management, but ensuring environmental safety requires monitoring leachate distribution and assessing geomembrane integrity. This case study outlines a case study that used geophysical methods to assess leachate seepage patterns and detect potential defects in geomembranes.

Ⅱ. Working methods and techniques
- Leachate Seepage Detection: Identify the spatial distribution of leachate within the landfill to evaluate its impact on surrounding soil and groundwater.
- Liner Integrity Assessment: Detect and locate any damages or defects in the geomembrane to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
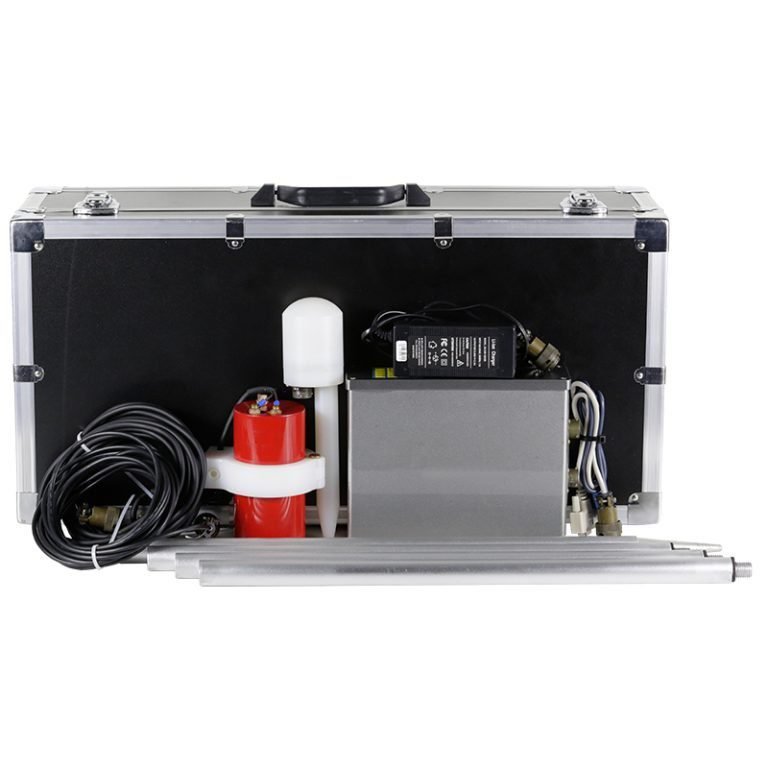
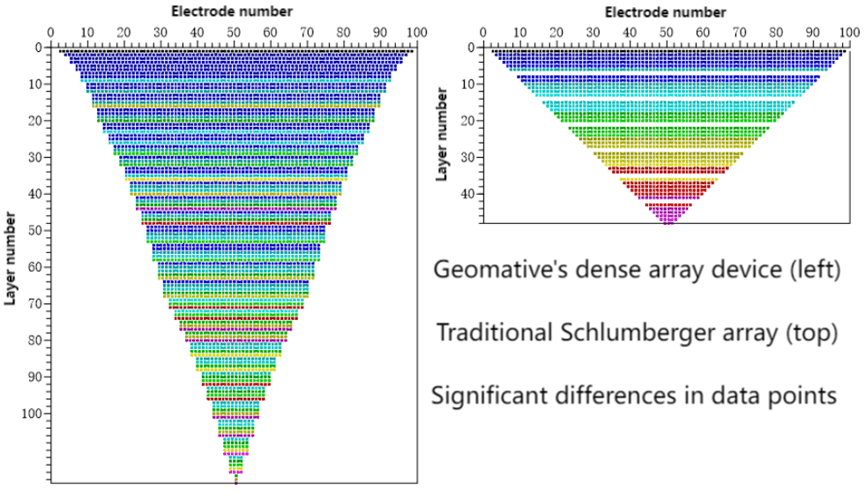
2. Equipment
The WGMD-4 High-density Electrical Method System developed by Geotech and WDZS-3 Multifunctional electrical water detector.

Ⅲ.Analysis and Results
2D Profile Analysis:
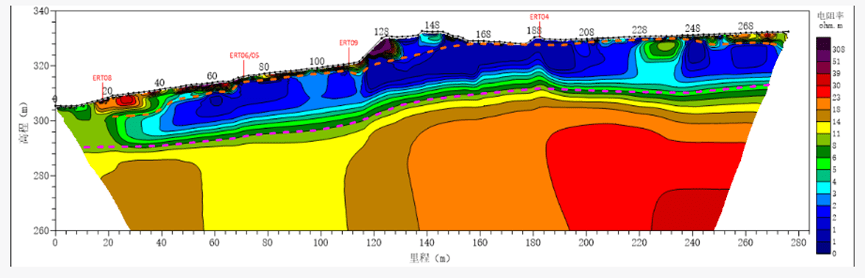
The profile data obtained using specialized landfill devices allowed for the identification of the geomembrane position and the leachate water level. Based on the measurement results, the resistivity distribution beneath the geomembrane is consistent and continuous, indicating good membrane integrity. Therefore, it can be inferred that the geomembrane in this area is intact, with no significant signs of leakage detected.
3D Model Insights:
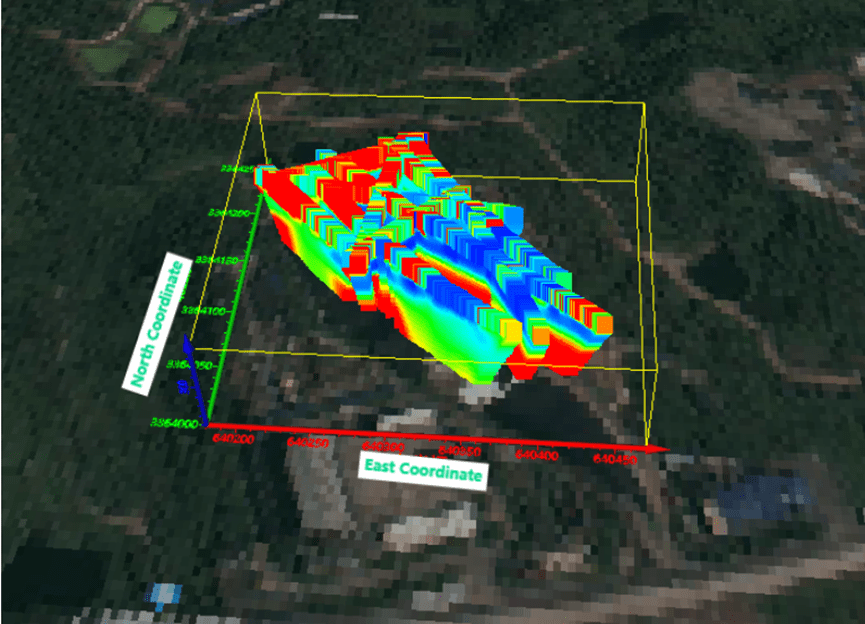
Using the profile data, a three-dimensional model was constructed to analyze the landfill contents, which are typically characterized by low resistivity. Areas with particularly low resistivity can be identified as leachate-rich zones. Based on prior physical property data, a boundary value of 4 Ω·m was used to delineate the leachate distribution. Additionally, the geomembrane interface was determined by referencing the profile morphology.
By analyzing the leachate distribution and porosity, the total volume of leachate at the site was estimated, providing a reliable basis for subsequent leachate extraction and landfill management efforts.
Ⅳ.Conclusion
Through this investigation, our company efficiently completed the challenging task of surveying a complex landfill environment, accurately obtaining data on leachate distribution and geomembrane integrity. Leveraging our self-developed high-density resistivity system, renowned for its high precision and strong adaptability, we provided comprehensive support for geomembrane integrity detection and leachate management. Additionally, our work offers valuable scientific and technical insights for future landfill expansion and safe operational planning.
Further reading | Technical solutions related to this article
In the field of resource exploration and engineering testing, accurate data is the key to success. As an innovator of resource and environmental instruments, Geotech has always taken high-precision electrical exploration technology as its core to provide reliable solutions for global users.
If you want to learn more about how the [Electrical Exploration System (ERT)] can help mineral exploration and geological research, please click on the electrical instrument product page to explore details, or visit Geotech’s official website to view the full range of exploration equipment (covering more than ten categories of products such as magnetometers, seismic nodes, and geological radars). Our technical team is on call at any time to customize scientific solutions for your project – making unknown strata a controllable data map.
FAQ
The double tap has a large current and can be used for IP testing to get more accurate data.
High-density apparent resistivity method is an array prospecting method, also known as automatic apparent resistivity system, which is developed from direct current method. Its function is equivalent to the combination of quadrupole sounding and electrical profiling method. The artificial electric field is formed by supplying electricity to the underground through electrodes. The distribution of the electric field is closely related to the distribution of the resistivity of the underground rock and soil medium. By measuring the artificial electric field at different parts of the surface, the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the underground medium is understood, and the underground geological structure is inferred and interpreted based on the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the rock and soil medium.
The principle of high-density electrical method is the same as that of traditional resistivity method. It is a combination method of multiple devices and multiple pole distances that integrates electrical depth sounding and electrical profiling method, which can obtain the conductivity characteristics of two-dimensional underground media. It has the characteristics of multi-device data acquisition in one pole arrangement, and highlighting abnormal information by obtaining ratio parameters, which greatly increases the amount of collected data, improves work efficiency, and ensures the accuracy and reliability of the pole running process.
This method is particularly sensitive to the water content of the surrounding rock. If the surrounding rock is broken and contains water, its apparent resistivity is significantly reduced. The apparent resistivity of intact and hard rock and soil is significantly higher than that of the surrounding rock in the fault zone or broken zone and water-rich zone. This method has a clear principle and intuitive images. It is a geophysical method with high resolution. In recent years, with the improvement of computer data acquisition technology, the exploration efficiency has been greatly improved, the coverage area and detection depth of the profile have been increased, reliable data can be obtained in a strong interference environment, the signal-to-noise ratio has been greatly improved, and the geological body can be accurately detected. This method has been widely and successfully applied in engineering and hydrogeological exploration and exploration of mineral and water resources.
(1) Application in coalfield and mine goaf detection
(2) Non-destructive detection of termite nests in dam foundations
(3) Karst and foundation surveys of railways, roads and tunnels
(4) Delineation of stratum lithology boundaries
(5) Survey of the leakage range of landfills
(6) Ancient tomb surveys
(7) Detection of sewage pipes
(8) Non-destructive testing of leakage in reservoirs and river dams
(9) Detection of bedrock fracture zones
(10) Soil salinity and water quality surveys
(11) Detection of ancient tunnels, air-raid shelters, metal burial sites, etc.
(1)The high-density resistivity method is based on the resistivity method, so it is suitable for all underground explorations with obvious conductivity differences;
(2)Any medium underground will have a weak polarization potential at the moment of power on and off, which will affect our measurement of the true potential difference. When the electrode distance is small, the loop current is large, which has little effect on the measurement results; when the electrode distance is too large, the interference potential is close to the effective potential, which has a greater impact on the measurement results. Therefore, due to the influence of the power supply electrode distance, the exploration depth cannot be too large, generally within 100m. When the conductivity of the soil medium is good, it can be appropriately increased, and the exploration depth in the soil medium with poor conductivity is appropriately smaller;
(3)It is generally less used in cities, near large transmission lines, etc. due to site restrictions and industrial stray current interference; 4. In areas such as concrete pavements and exposed bedrock surfaces, it is also less used due to the difficulty of electrode layout.
-1.png)






