Welcome to Geotech!

Magnetic Gradient Surveying + AI: Revolutionizing Geophysical Exploration Practices
TIPS:Magnetic gradient surveying, a key geophysical tool, gets a powerful boost from AI. AI – enhanced gradient measurement and ML in magnetic exploration drive efficient data processing. It enables intelligent anomaly detection and automated interpretation, revolutionizing geophysical practices. Magnetic gradient surveying + AI paves the way for future – proof exploration, showcasing innovation in earth science methods.

Ⅰ. Introduction to Magnetic Gradient Surveying Basics
Magnetic gradient surveying is a cornerstone in geophysical exploration. It involves measuring variations in the Earth’s magnetic field over short distances to detect subsurface anomalies. These anomalies can indicate the presence of mineral deposits, geological structures like faults, or even archaeological features. Traditionally, this process relied on manual data analysis and interpretation, which was time – consuming and prone to human error.
But now, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming magnetic gradient surveying. AI – enhanced gradient measurement, as part of magnetic gradiometry with artificial intelligence, is making the process more efficient and accurate. This fusion is not just a minor upgrade; it’s a complete overhaul of how geophysicists approach exploration, promising to lead the way in new earth science methods and advanced exploration technology.
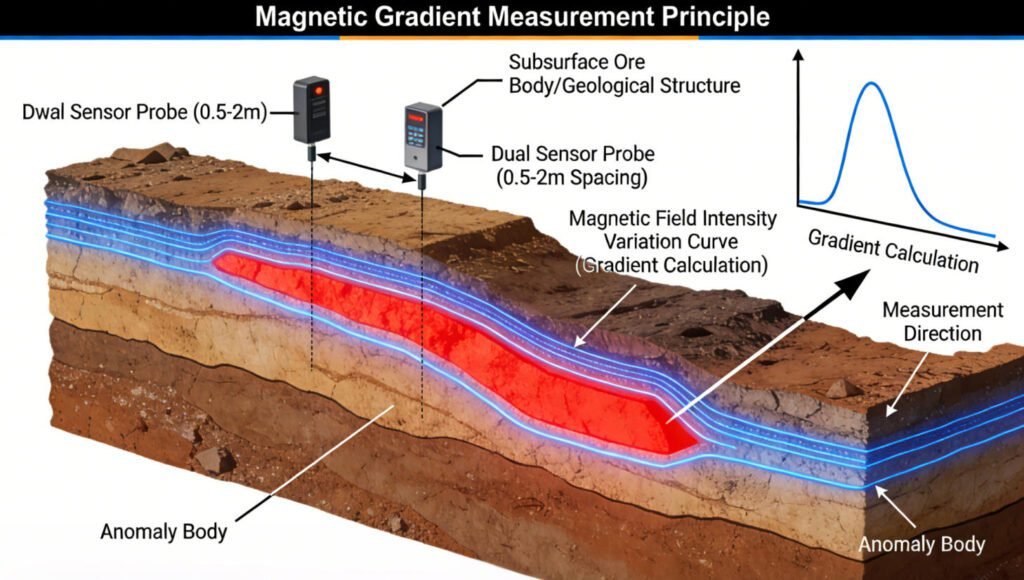
Ⅱ. AI Integration in Magnetic Gradient Surveying
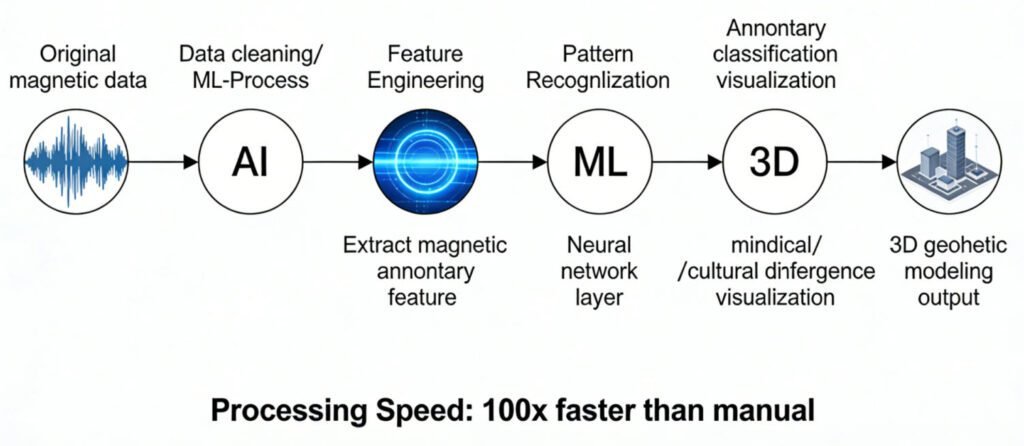
1. Machine Learning in Magnetic Survey (ML applications in magnetic exploration)
Machine learning algorithms are at the heart of this transformation. In magnetic exploration, ML applications are used to analyze vast amounts of magnetic gradient data. These algorithms can identify complex patterns in the data that would be impossible for a human to detect.
For example, a machine – learning model can be trained on historical magnetic survey data, along with information about known mineral deposits or geological structures. Once trained, it can then analyze new survey data in real – time, predicting the likelihood of finding similar deposits or structures. This AI – driven data analysis is much faster than traditional methods and can process data from multiple survey sites simultaneously.
2. Intelligent Anomaly Detection (AI – based magnetic anomaly finding)
Intelligent anomaly detection is another key area where AI shines in magnetic gradient surveying. Smart irregularity identification, or AI – based magnetic anomaly finding, uses AI algorithms to sift through survey data and pick out significant magnetic anomalies.
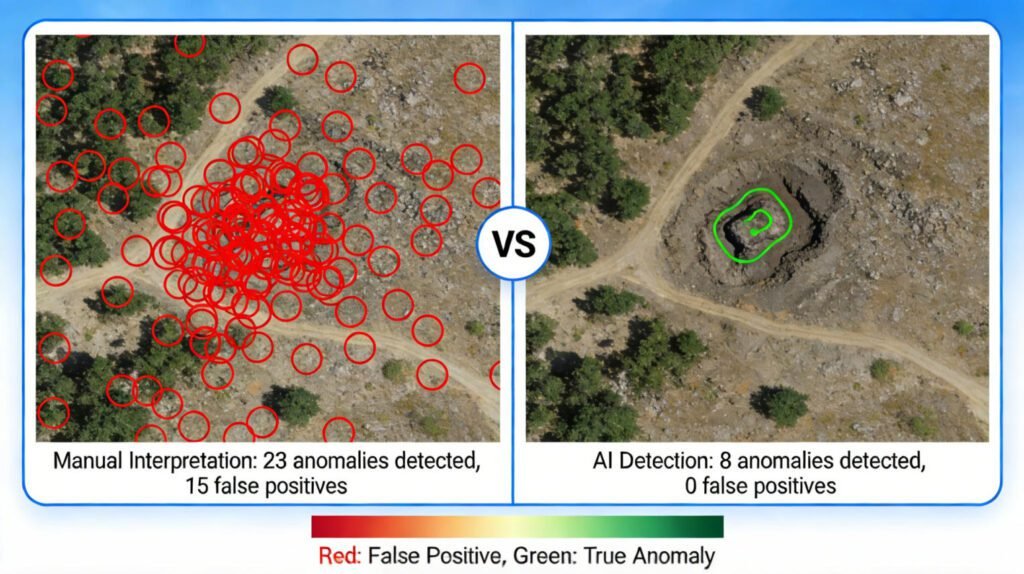

In traditional methods, geophysicists would have to manually examine data plots, looking for deviations from the norm. With AI, the process is automated and more precise. The AI can be programmed to recognize different types of anomalies, such as those caused by mineralization versus those caused by cultural interference (like buried metal structures). This not only saves time but also reduces the number of false positives, leading to more targeted and successful exploration efforts.
3. Automated Data Interpretation (AI – powered result evaluation)
Automated data interpretation is a game – changer. In the past, interpreting magnetic gradient survey data required a high level of expertise and a lot of time. Self – service data analysis, or AI – powered result evaluation, allows for quick and accurate interpretation of survey results.
AI algorithms can take raw magnetic gradient data and convert it into actionable insights. For instance, they can generate 3D models of subsurface structures based on the data, showing geophysicists the likely shape and location of potential targets. This automation means that even less – experienced geophysicists can benefit from high – quality data interpretation, making magnetic gradient surveying more accessible to a wider range of professionals in the geoscience community.
Ⅲ. Practical Achievements of Magnetic Gradient Surveying + AI
1. Data Processing Advancements
The integration of AI has led to significant advancements in data processing. Magnetic gradiometry with artificial intelligence can handle large – volume survey data sets with ease. For example, in a large – scale mineral exploration project, the amount of magnetic gradient data collected can be overwhelming. But with AI algorithms, this data can be processed in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
These algorithms can also clean and preprocess the data, removing noise and artifacts that can skew the results. This leads to more accurate and reliable data, which is essential for making informed decisions in geophysical exploration.
2. Anomaly Detection Improvements
In terms of anomaly detection, the results have been remarkable. AI – based magnetic anomaly finding has increased the detection rate of significant anomalies while reducing false positives. In archaeological exploration, for example, it can detect very subtle magnetic anomalies that may indicate the presence of ancient structures or artifacts.
In mineral exploration, it can pick out the weak magnetic signatures of deep – seated mineral deposits that traditional methods might miss. This has the potential to unlock new mineral resources and expand our knowledge of the Earth’s subsurface.
3. Impact on Geophysical Technology Innovation
The fusion of magnetic gradient surveying and AI is driving innovation in geophysical technology. Future – proof geophysical techniques, or innovative earth science methods, are emerging as a result of this integration. New types of magnetic gradient sensors are being developed that are better suited for use with AI algorithms, and new software platforms are being created to handle the data analysis and interpretation more effectively.
This technological innovation is not only improving the efficiency of geophysical exploration but also opening up new avenues of research and discovery in the earth sciences.
Ⅳ. Future Prospects of Magnetic Gradient Surveying + AI
1. Further Integration with Emerging Technologies
The future holds even more promise as magnetic gradient surveying + AI integrates with other emerging technologies. For example, the combination with Internet of Things (IoT) devices could enable real – time, continuous magnetic gradient monitoring in remote areas. Drones equipped with magnetic gradient sensors and AI – powered data processing capabilities could revolutionize aerial geophysical surveys, allowing for faster and more comprehensive coverage of large areas.
This integration with other technologies will continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in geophysical exploration.

2. Expanded Applications in Different Fields
The applications of magnetic gradient surveying + AI are not limited to traditional geophysical exploration. In environmental monitoring, it can be used to detect changes in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by processes like soil erosion or groundwater contamination. In urban planning, it can help in detecting buried infrastructure and assessing geological risks.
As AI algorithms become more sophisticated and magnetic gradient surveying techniques improve, the range of applications will only continue to grow.
3. Training and Skill Development in the Geoscience Community
With the increasing use of AI in magnetic gradient surveying, there is a need for training and skill development in the geoscience community. Geophysicists need to learn how to use AI algorithms effectively, how to interpret the results generated by these algorithms, and how to integrate AI – powered tools into their existing workflows.
Educational institutions and professional organizations are starting to offer courses and training programs in this area, ensuring that the next generation of geoscientists is well – equipped to take advantage of these new technologies.
Reference
- WIKI:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistivity_tomography
- Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) https://seg.org/
- Society of Environmental and Engineering Geophysicists (EEGS) https://www.eegs.org/
- Geology and Equipment Branch of China Mining Association http://www.chinamining.org.cn/
- International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) http://www.iugs.org/
- European Geological Survey Union (Eurogeosurveys) https://www.eurogeosurveys.org/
-1.png)



