Welcome to Geotech!

ERT Equipment: Complete Resistivity Tomography Guide
ERT equipment has revolutionized geophysical exploration by providing non-invasive subsurface imaging capabilities. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) represents one of the most versatile geophysical methods available today, using advanced resistivity meters to map underground structures with remarkable precision.
This comprehensive guide explains what ERT equipment is, how it works, and why it has become indispensable for geotechnical engineers, hydrogeologists, and mineral exploration teams worldwide.
What is ERT Equipment?
ERT equipment consists of integrated geophysical instrumentation designed to measure earth resistivity distribution. The system typically includes:
- Resistivity meter (data logger) with high-precision A/D converters
- Electrode arrays (stainless steel or non-polarizable Ag/AgCl)
- Multi-core cables with intelligent switching systems
- Inversion software for 2D/3D data processing
By injecting direct current into the ground through electrode arrays and measuring voltage differences, electrical resistivity tomography equipment generates detailed subsurface models. Modern high-density ERT systems can achieve exploration depths from 5 meters to 1,500 meters, depending on electrode configuration.
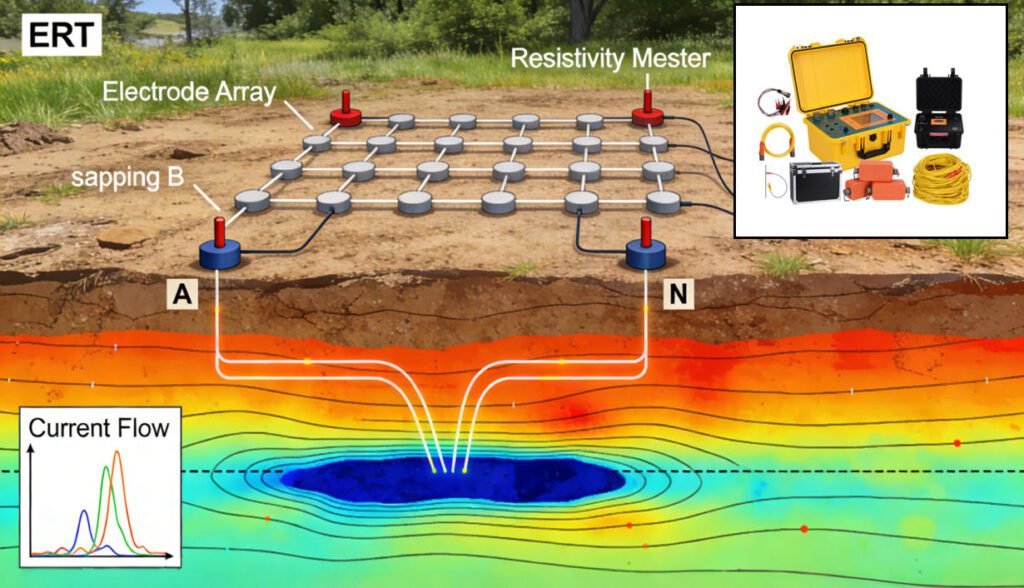
Key Advantages of ERT Equipment
1. Non-Invasive Investigation Unlike drilling, ERT survey equipment requires no ground penetration, making it ideal for environmentally sensitive areas, urban infrastructure, and archaeological sites.
2. Multi-Scale Detection Adjustable electrode spacing allows portable ERT equipment to investigate targets ranging from shallow engineered structures (2-10m) to deep geothermal reservoirs (>500m).
3. Parameter Integration Advanced resistivity and IP equipment combines induced polarization (IP) measurements with resistivity data, enabling discrimination between metallic ores and conductive clays.
ERT Equipment vs. Other Geophysical Methods
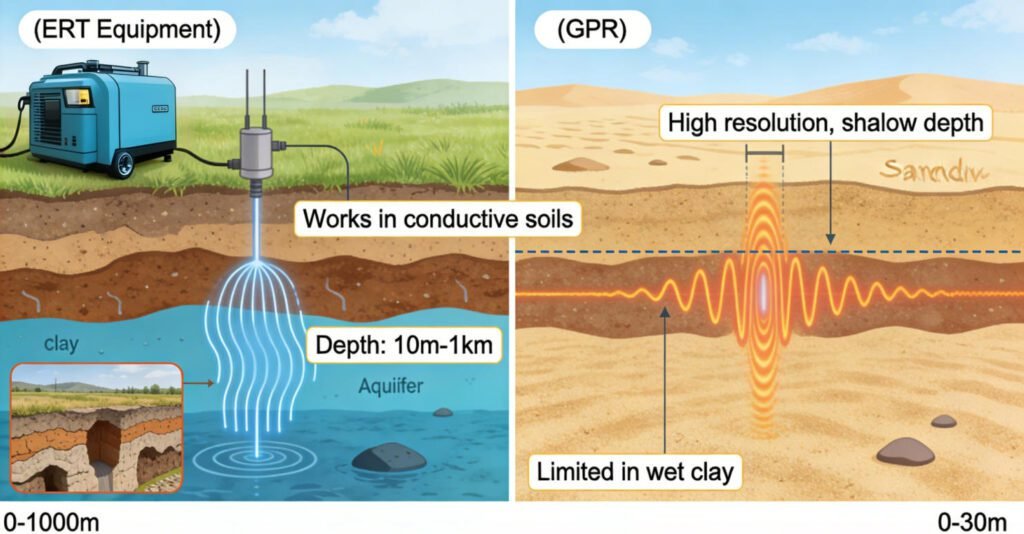
ERT Equipment vs. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
| Feature | ERT Equipment | GPR Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Depth Range | 10m–1km (electrode dependent) | 0.1–30m (conductivity limited) |
| Best For | Groundwater, karst, geology | Pipes, cables, shallow archaeology |
| Soil Suitability | All soil types (high conductivity OK) | Poor in clay/wet soils |
| Data Output | Quantitative resistivity values | Qualitative reflection profiles |
Case Study: In landfill leak detection, 3D ERT equipment successfully mapped contaminant plume distribution while GPR pinpointed surface penetration points.
ERT vs. Seismic Exploration
While seismic equipment measures elastic wave velocities, electrical resistivity tomography equipment measures ground conductivity. ERT tools excel at:
- Aquifer delineation and water content mapping
- Clay layer identification
- Foundation stability assessment
For comprehensive landslide monitoring, engineers often combine ERT survey systems (groundwater tracking) with seismic surface wave methods (shear strength analysis).
Types of ERT Equipment and Technologies
2D vs. 3D Resistivity Equipment
2D ERT Systems
- Linear electrode arrays
- Rapid deployment for profile surveys
- Ideal for fault mapping and cavity detection
3D ERT Equipment
- Grid-based electrode arrangements
- Volumetric resistivity models
- Essential for complex karst terrain and mining applications
Example: A coal mine in Shanxi utilized GIM Series to map groundwater pathways ahead of tunneling operations.
High-Density Electrical Method
Modern high-density ERT equipment features:
- Automatic electrode switching (no manual reconfiguration)
- Multi-array capability (Wenner, Schlumberger, Dipole-Dipole)
- 120dB+ dynamic range for high noise environments
Systems like the Electrical-instrument support 1,000+ electrodes, enabling efficient large-scale surveys.
Induced Polarization (IP) Integration
IP-capable ERT equipment measures both resistivity and chargeability, critical for:
- Mineral exploration: Detecting sulfide ore bodies
- Environmental monitoring: Tracking heavy metal contamination
- Geothermal exploration: Identifying alteration zones
ERT Equipment Selection Guide
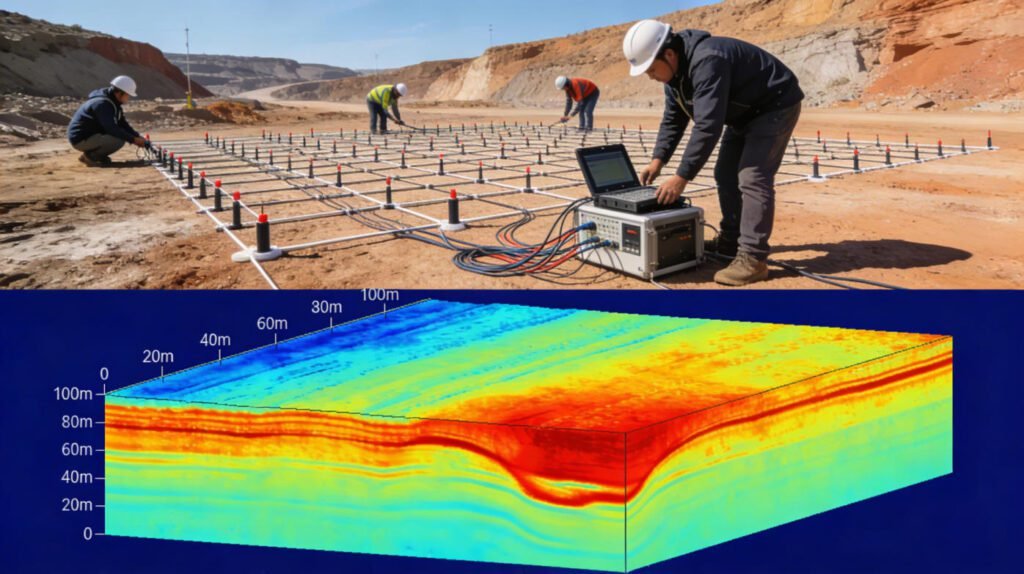
Key Components to Consider
1. Data Logger Specifications
- A/D Resolution: 24-bit minimum for professional surveys
- Channels: 10-channel for small projects, 60-120+ for 3D ERT
- Accuracy: <1% error margin for engineering applications
2. Electrode Systems
- Stainless steel: Cost-effective for general soil resistivity surveys
- Ag/AgCl non-polarizable: Essential for IP measurements and high-precision work
3. Cable Configuration
- Intelligent cables: Built-in switching for rapid acquisition
- Extension capability: Support for 1,500m+ penetration depth
Applications by Industry
| Industry | ERT Application | Recommended Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Foundation leakage, void detection | High-density 3D ERT + borehole systems |
| Environmental | Contaminant plume mapping | <a href=”/service/environmental-geophysics/”> |
| Mining | Ore body delineation | IP-integrated resistivity meters |
| Hydrogeology | Aquifer characterization | Deep-penetration 2D/3D systems |
Advanced ERT Techniques
Forward Modeling and Inversion
Forward Modeling Software: Tools like RES2DMOD simulate theoretical responses, helping optimize survey design before fieldwork.
Inversion Algorithms:
- Smoothness-constrained: Best for layered geological structures
- Robust inversion: Handles noisy data from challenging terrains
- Joint inversion: Combines ERT with seismic or electromagnetic data
Cross-Hole and Borehole ERT
Borehole ERT equipment overcomes surface limitations by placing electrodes in drill holes, providing high-resolution imaging between boreholes for:
- Dam foundation integrity assessment
- Tunnel advance geological prediction
- Deep mineral deposit delineation
Future of ERT Equipment
1. AI-Driven Data Interpretation Machine learning algorithms now automate anomaly detection, reducing processing time by 70% while improving consistency.
2. Drone-Deployed ERT Lightweight portable ERT systems (under 15kg) enable rapid deployment in mountainous or inaccessible terrain.
3. 4D Time-Lapse Monitoring Permanent ERT monitoring systems track seasonal groundwater changes, dam seepage, and environmental remediation progress.
FAQ: ERT Equipment Essentials
Q: What is ERT equipment used for? A: ERT equipment is used for non-invasive subsurface imaging in geotechnical investigations, groundwater exploration, mineral prospecting, and environmental monitoring. It creates 2D or 3D models of ground resistivity without drilling.
Q: How much does professional ERT equipment cost? A: Professional electrical resistivity tomography equipment ranges from $15,000 for basic 2D systems to $80,000+ for advanced 3D high-density systems. The GIM Series offer professional-grade 1,500m penetration at competitive pricing.
Q: What’s the difference between ERT and IP equipment? A: While ERT equipment measures resistivity, IP (Induced Polarization) equipment measures chargeability. Modern systems like the GIM Series integrate both technologies, providing comprehensive data for mineral exploration and environmental assessment.
Q: How deep can ERT equipment investigate? A: Standard portable ERT equipment reaches 50-100m. Advanced systems with optimized electrode arrays can achieve 1,000m+ for deep geothermal or mining applications. Depth depends on electrode spacing and ground conductivity.
Q: Is ERT equipment better than GPR? A: ERT survey equipment excels in conductive environments (clay, water) where GPR fails. GPR offers higher resolution for shallow (<10m) dry conditions. Many projects use both methods complementarily.
Recommended ERT Equipment
Geotech GIM Series: Professional Resistivity & IP System
For engineers seeking reliable ERT equipment, the GIM Series offer:
- Multi-Function: Natural potential, 1D/2D/3D resistivity, and induced polarization
- Deep Penetration: 24-bit precision with 1,500m investigation depth
- Rugged Design: IP67 waterproof, -20°C to +60°C operating range
- Efficiency: 10-channel simultaneous acquisition with rolling measurement mode
- Software Compatibility: Exports to Res2DInv, EarthImager, and Surfer formats
Ideal Applications:
- Groundwater exploration and pollution monitoring
- Mineral ore body location (sulfides, oxides)
- Geotechnical engineering and cavity detection
- Tunnel and foundation stability assessment
Contact US for ERT equipment specifications, rental options, or application engineering support.
Reference
- WIKI:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistivity_tomography
- Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) https://seg.org/
- Society of Environmental and Engineering Geophysicists (EEGS) https://www.eegs.org/
- Geology and Equipment Branch of China Mining Association http://www.chinamining.org.cn/
- International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) http://www.iugs.org/
- European Geological Survey Union (Eurogeosurveys) https://www.eurogeosurveys.org/
-1.png)


