Welcome to Geotech!

【WGMD-4 】Application of geophysical methods in the investigation of organic contaminated sites
Description
Ⅰ.Introduction
The survey site was a decommissioned chemical plant in Nantong, Jiangsu Province, with a survey area of 120,000 square meters. Traditional drilling and sampling engineering has a large amount of work and a long cycle. Using high-density resistivity method and induction electromagnetic method, a wide range of surface measurements are carried out to determine the pollution level area and its depth range. Finally, combined with the results of the sampling analysis, the coverage of the entire underground space is detected, and the underground pollution and the current situation of the formation are described by the specific images of the geophysical results.
The focus of the work is to detect the distribution of soil and groundwater pollution in the survey area, and provide more objective decision-making basis for the remediation unit.
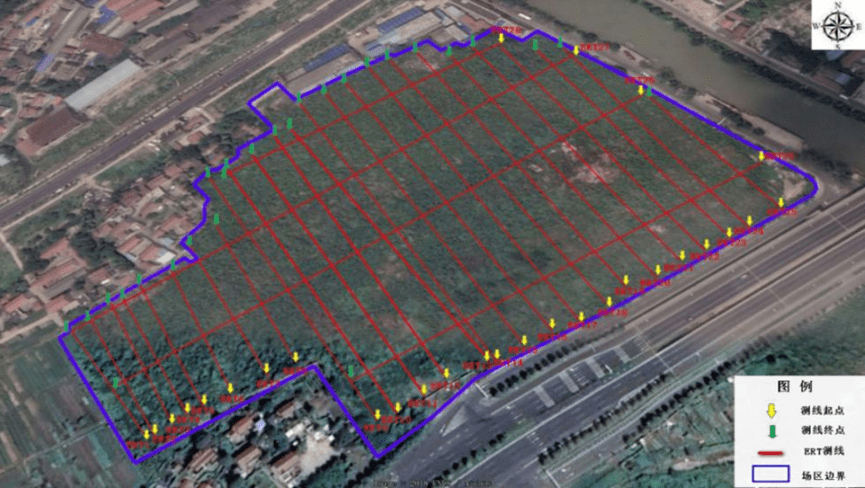
Ⅱ.Survey work planning
In order to find out the pollution distribution in the investigation area, a comprehensive induction electromagnetic survey is conducted for the site planning this time, and the conductivity distribution map within the site is drawn, and the high-density resistance method is applied to the high-conductivity block of the induction electromagnetic method. To assess the vertical depth of soil pollution, the survey completed the induction electromagnetic test area of about 120,000 square meters, high-density electrical method line 29 and background line, a total of 6430 meters.
Ⅲ.Working methods and techniques
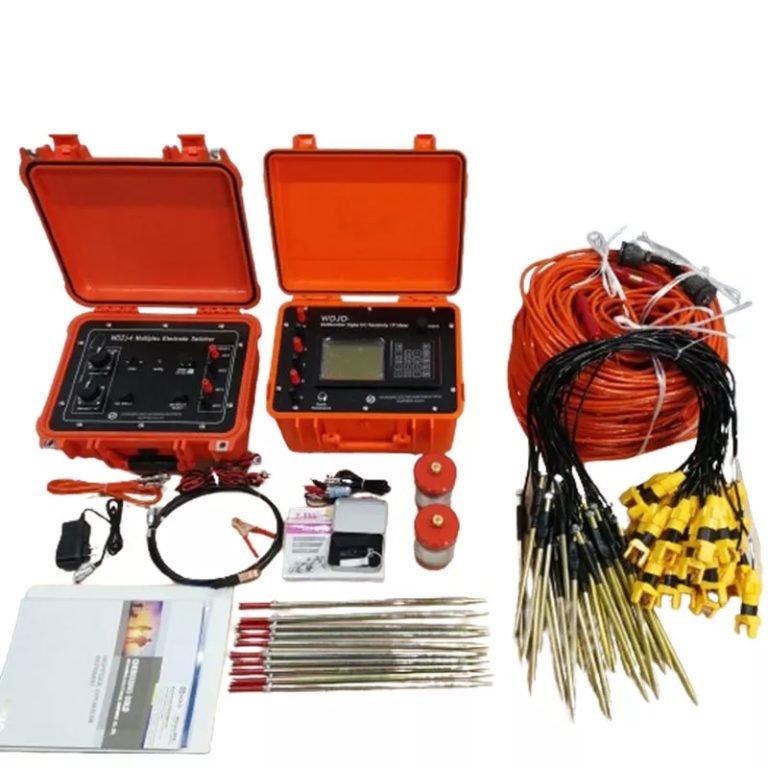
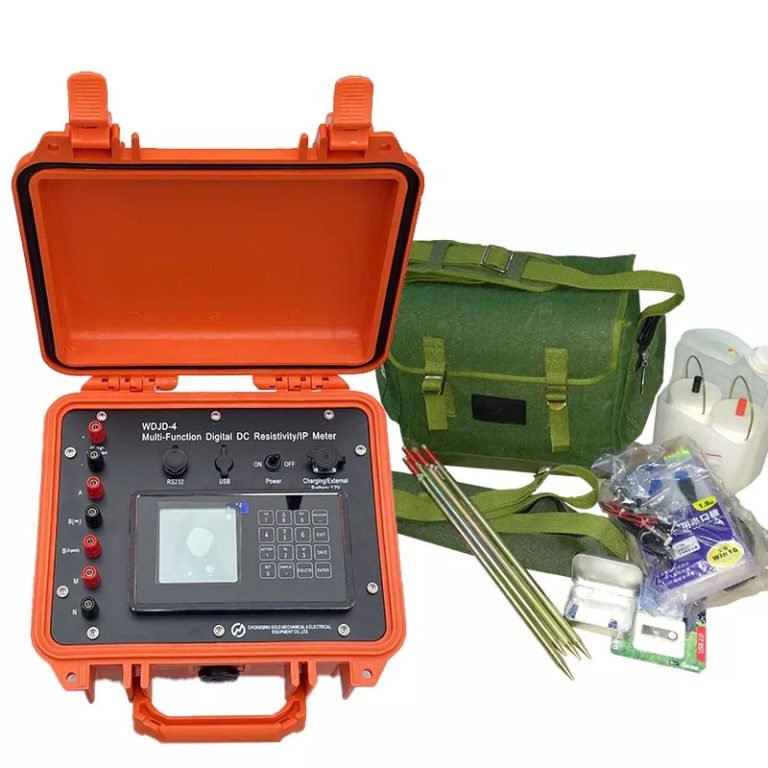
1. Equipment
The WGMD-4 High-density Electrical Method System developed by Geotech and WDZS-3 Multifunctional electrical water detector.
Resistivity imaging: actively introduces DC current into the formation to measure the potential difference, and inverts the calculated material to depict the 2D or 3D structure of the formation with a resistivity distribution.
3. Technology
Inductive electromagnetic method with GPS positioning immediately when testing, sweeping the whole field.
High-density electrical method, the electrode device uses a four-stage device. The minimum spacing factor is 1, the electrode point is 2 meters, the detection target depth is within 20 meters, and the average pollution depth is estimated to be 0-20 meters.
Ⅳ.Analysis and conclusion
Inductive electromagnetic method results
According to the EM detection results, the color gradation in the result graph represents high conductivity (low resistivity) in red, while the blue-violet color is in low conductivity range.
According to the on-site records, the blocks are (1), (2), (3), (4), (5), (6), which may be the main pollution potential areas, of which blocks (1), (2) ), (3), (5) are heavy pollution potential areas, and blocks (4) and (6) are relatively light pollution potential areas.


High-density electrical method results
Line 14 shows that the overall groundwater level in the survey area is shallow and the average depth is about 1.6 meters. The overall anomalous results show a low-resistance distribution, which may lead to leakage of wastewater or acid in the production process or later, causing pollution of inorganic salts into groundwater, and moving along the deeper layers of the groundwater flow, resulting in NAPLS pollutants (if There are also leaks) that are highly concealed by highly conductive waste water and inorganic salt materials, thereby exhibiting low resistance characteristics.

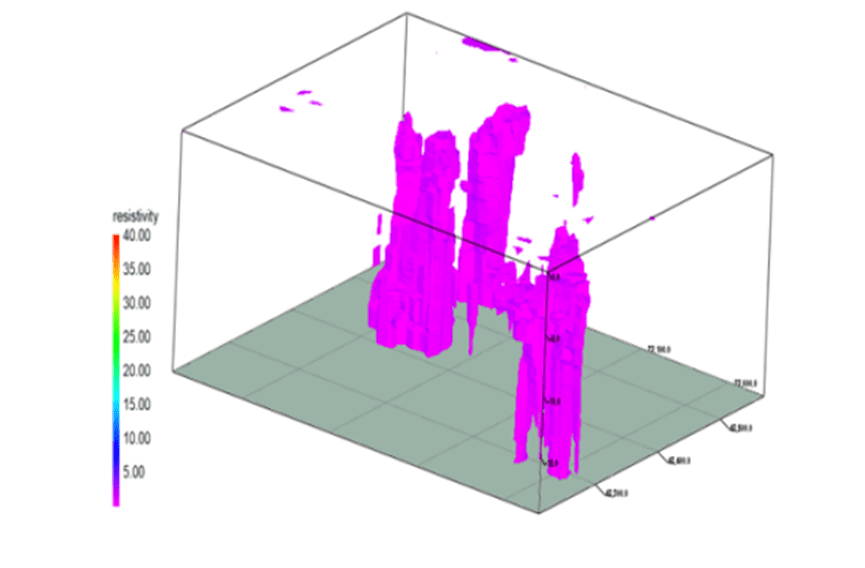
In order to more accurately observe the pollution distribution state of the measurement area, the resistivity results of the high-density resistivity method line 1 to line 29 are composed into a grid diagram to obtain a comprehensive high-density resistivity distribution result map of the field region.
Combined with the results of induction electromagnetic method, the abnormal region presented by ERT is basically consistent with the high-conductivity anomaly exhibited by induction electromagnetic method, and the measurement results are mutually verified.
At the same time, the pollution of the whole survey area can be roughly divided into three parts, as shown in Figure 5-4, which are located in the southwest corner of the field, the northeast direction of the field and the middle area of the field.

Ⅴ.Conclusion
1. Through this survey, delineate the scope of key pollution.
2. 0-2 meters on the surface, should be building backfill.
3.In the key pollution area, the abnormal pollution depth can reach 21.4 meters deep.
4. Local pollution with the migration of groundwater, the depth of pollution even reached 44 meters.
Explore Revolutionary WGMD-4 Series Now
Visit Product Page Now :
WGMD-4 Distributed High-density Electrical Method System
WGMD-4 centralized high-density electrical method system
Whether you’re engaged in environmental monitoring, mineral exploration, or urban underground space development, the WGMD-4 Series electrical method system. Our product page features:
Explore Geotech Series Solutions
Discover our IP-Resistivity integrated systems at our web site, engineered for complex near-surface challenges.
FAQ
The double tap has a large current and can be used for IP testing to get more accurate data.
High-density apparent resistivity method is an array prospecting method, also known as automatic apparent resistivity system, which is developed from direct current method. Its function is equivalent to the combination of quadrupole sounding and electrical profiling method. The artificial electric field is formed by supplying electricity to the underground through electrodes. The distribution of the electric field is closely related to the distribution of the resistivity of the underground rock and soil medium. By measuring the artificial electric field at different parts of the surface, the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the underground medium is understood, and the underground geological structure is inferred and interpreted based on the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the rock and soil medium.
The principle of high-density electrical method is the same as that of traditional resistivity method. It is a combination method of multiple devices and multiple pole distances that integrates electrical depth sounding and electrical profiling method, which can obtain the conductivity characteristics of two-dimensional underground media. It has the characteristics of multi-device data acquisition in one pole arrangement, and highlighting abnormal information by obtaining ratio parameters, which greatly increases the amount of collected data, improves work efficiency, and ensures the accuracy and reliability of the pole running process.
This method is particularly sensitive to the water content of the surrounding rock. If the surrounding rock is broken and contains water, its apparent resistivity is significantly reduced. The apparent resistivity of intact and hard rock and soil is significantly higher than that of the surrounding rock in the fault zone or broken zone and water-rich zone. This method has a clear principle and intuitive images. It is a geophysical method with high resolution. In recent years, with the improvement of computer data acquisition technology, the exploration efficiency has been greatly improved, the coverage area and detection depth of the profile have been increased, reliable data can be obtained in a strong interference environment, the signal-to-noise ratio has been greatly improved, and the geological body can be accurately detected. This method has been widely and successfully applied in engineering and hydrogeological exploration and exploration of mineral and water resources.
(1) Application in coalfield and mine goaf detection
(2) Non-destructive detection of termite nests in dam foundations
(3) Karst and foundation surveys of railways, roads and tunnels
(4) Delineation of stratum lithology boundaries
(5) Survey of the leakage range of landfills
(6) Ancient tomb surveys
(7) Detection of sewage pipes
(8) Non-destructive testing of leakage in reservoirs and river dams
(9) Detection of bedrock fracture zones
(10) Soil salinity and water quality surveys
(11) Detection of ancient tunnels, air-raid shelters, metal burial sites, etc.
(1)The high-density resistivity method is based on the resistivity method, so it is suitable for all underground explorations with obvious conductivity differences;
(2)Any medium underground will have a weak polarization potential at the moment of power on and off, which will affect our measurement of the true potential difference. When the electrode distance is small, the loop current is large, which has little effect on the measurement results; when the electrode distance is too large, the interference potential is close to the effective potential, which has a greater impact on the measurement results. Therefore, due to the influence of the power supply electrode distance, the exploration depth cannot be too large, generally within 100m. When the conductivity of the soil medium is good, it can be appropriately increased, and the exploration depth in the soil medium with poor conductivity is appropriately smaller;
(3)It is generally less used in cities, near large transmission lines, etc. due to site restrictions and industrial stray current interference; 4. In areas such as concrete pavements and exposed bedrock surfaces, it is also less used due to the difficulty of electrode layout.
-1.png)





