Welcome to Geotech!

【WGMD-4】Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) Method in Borehole Tests in Tajikistan
- Cases, Engineering Exploration Cases
- 23 views
Description
Ⅰ.Introduction
The local climate in Tajikistan is highly variable, and soil salinization and alkalization are extremely severe. This has led to scarce natural vegetation along the entire river. The situation also contributes to river dam problems and serious soil erosion. The local land mainly consists of soft soil, with numerous stones of various sizes. Soil slides occur frequently at the site. In the plane, except for the soft clay and reinforced materials previously used in infrastructure layout, the surrounding area is reinforced and rigidly fixed with soft soil engineering materials. The layout is mainly in horizontal and surface forms.

Ⅱ. Purposes of project implementation
(1)To comprehensively understand the underlying structure of the entire plane, which is crucial for facilitating the selection of late – stage mining equipment and formulating work plans.
(2)To precisely define the location of rock – layer cracks predicted by experts. This information provides valuable support for the repair project.
Ⅲ.Survey method
Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) Method:The contrast between the physical properties of chargeability and resistivity of the environment involved makes it possible to delimit the deposition environment to identify the area of accumulation of the gold ore, making it possible to identify potential potential sources through drill holes.
They provide a true “tomography” of the subsoil, providing essential information for the prospects.
Ⅳ.Equipment
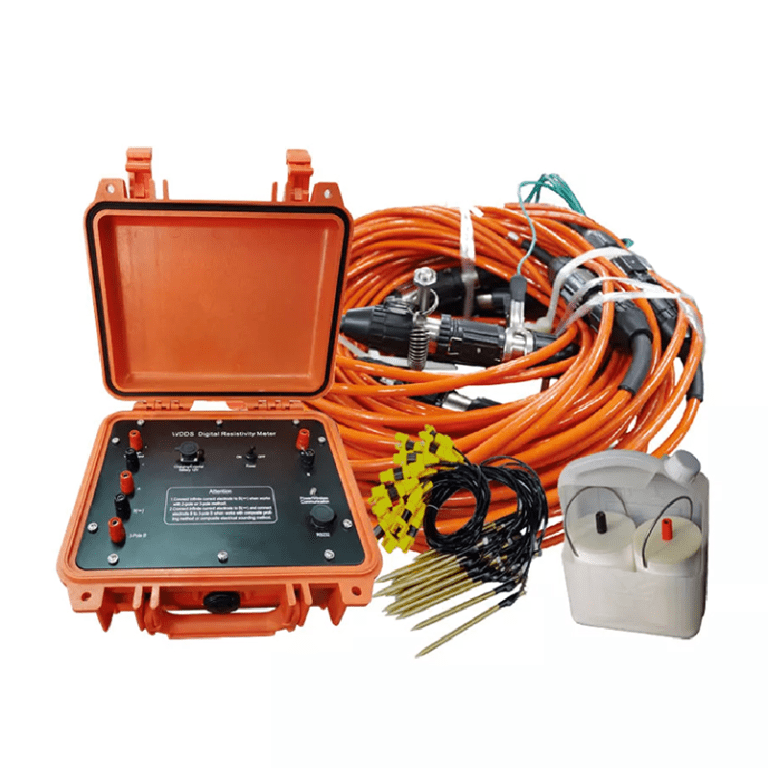
The survey mission used Geotech’s WGMD-4 centralized high-density electrical method system【Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) Method】, with 24 non-polarized electrodes in the area where the metal ore exists.
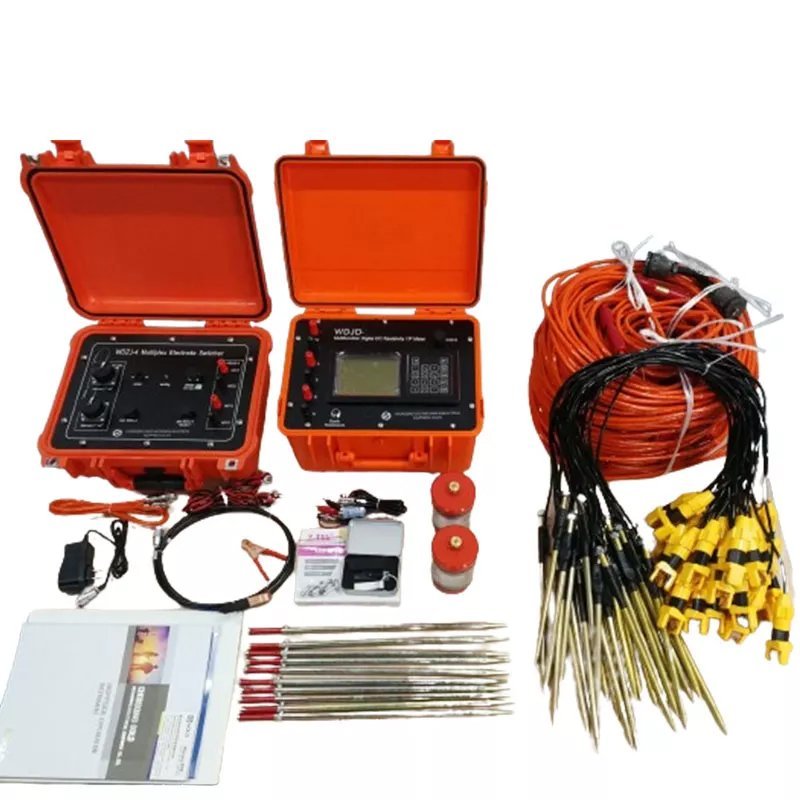
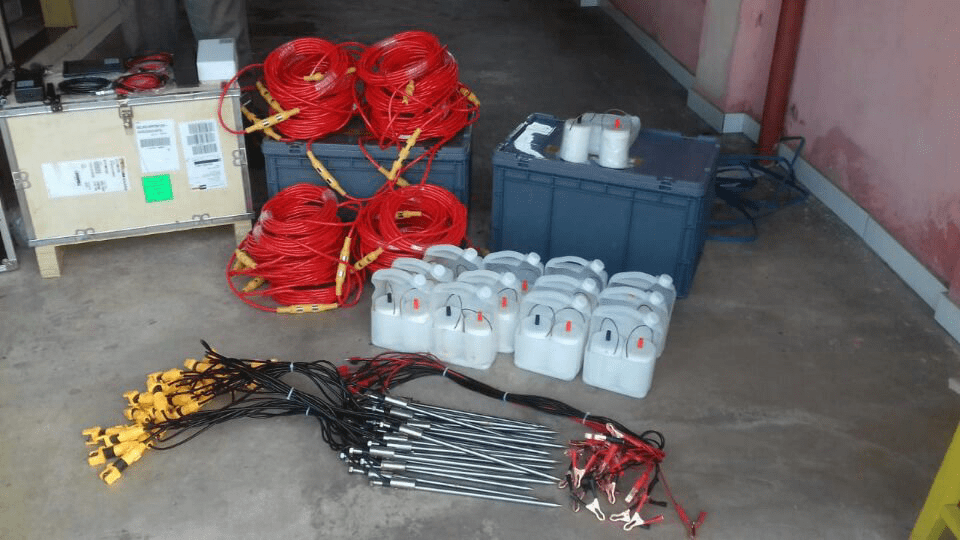


Ⅴ.Project implementation
Details of test Process:
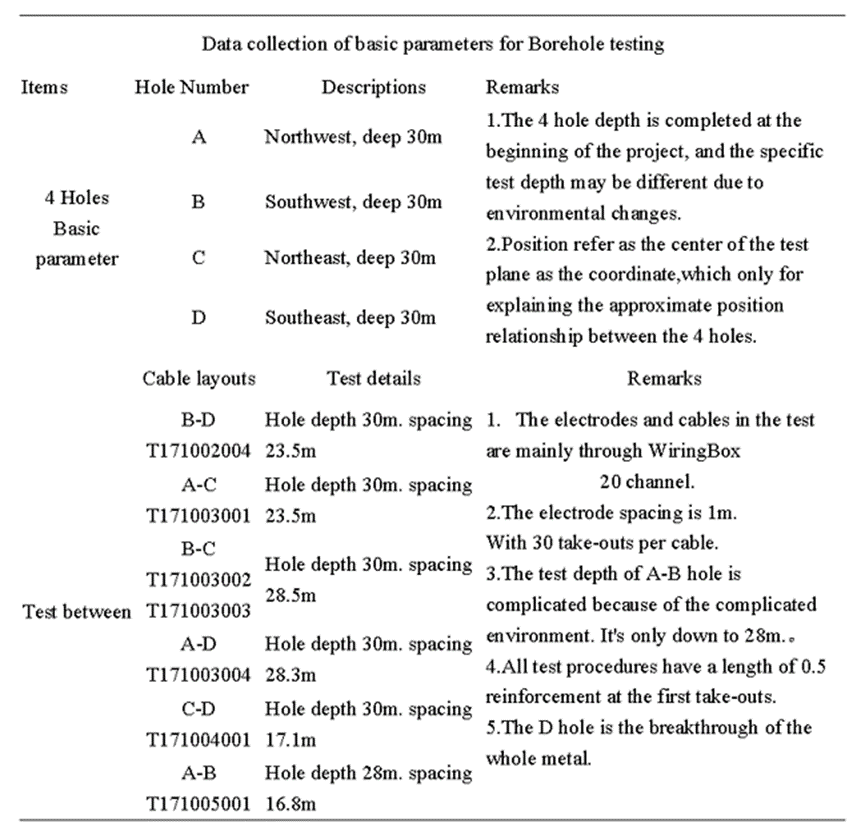
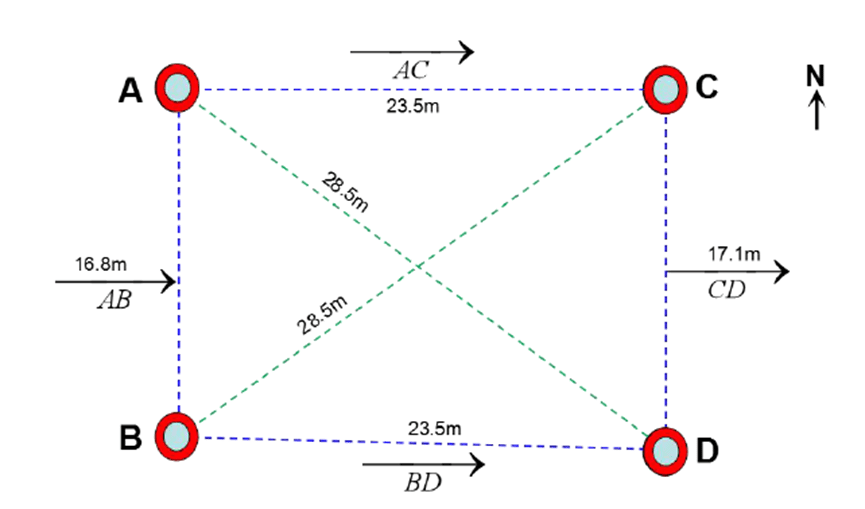
Ⅵ. Analysis of the Results
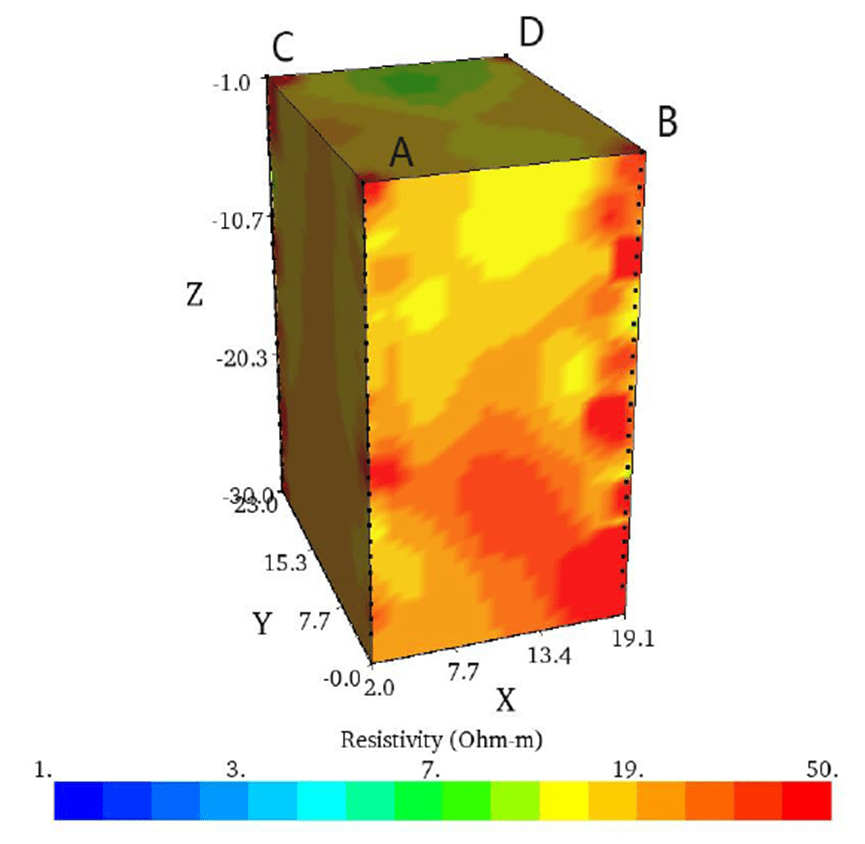
Analysis of the Results of 4 – Holes Test Data under the Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) Method.
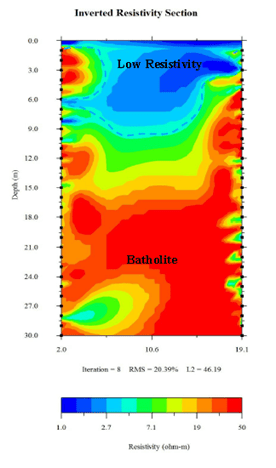
The area around the test site is composed of gravel and soft soil, resulting in a relatively high resistivity reaction in the formation. When measured in rainy conditions or areas with surface water, the surface shows relatively low resistivity. If there are cracks, the low – resistivity water can penetrate, which helps to distinguish fractures from the rock.
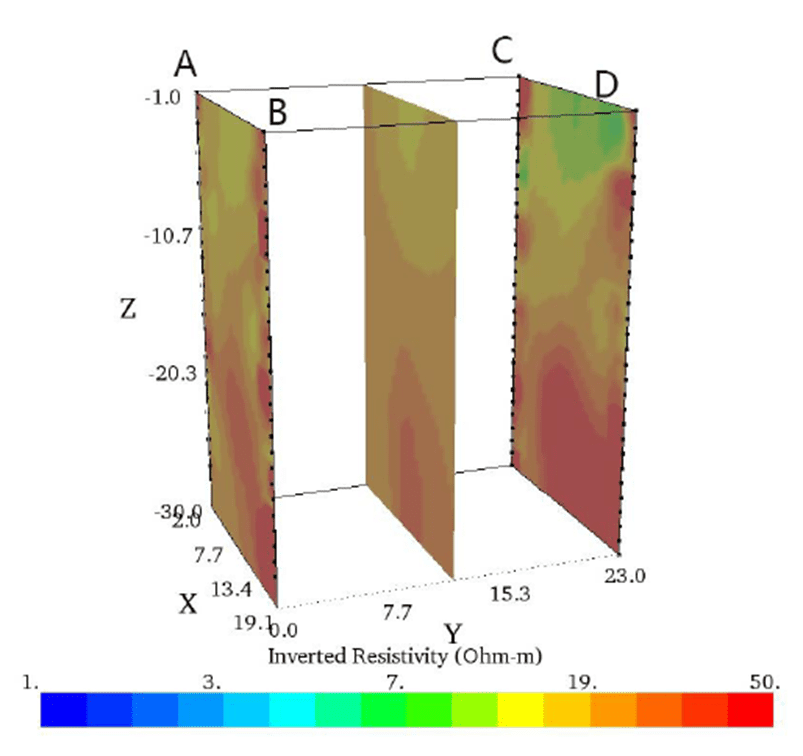
The surface profile of the AC section of around 0~1 meters are the low resistivity layer with the value is 1~5 ohmm.Extending from the surface to the depth of 15 meters, the depth of 24 meters(some partial). At a depth of 24.5 meters, the local high resistivity value is 16 ohmm.The surface profile of the BD section around 0~14meters are low resistivity layer, the depth of the section is 15.5 meters high resistivity.
The surface profile of the BC section around 0~11 meters are low resistivity layer, the depth of the section is 16 meters high resistivity. The surface profile of AD section around 0 to 15.5 meters are low resistivity layer, the depth is 24 meters high resistivity.
The 0~9 meter surface of the CD profile is a low resistivity layer with a depth of 14 meters and a high resistivity. Line AB section depth 11 meters high resistivity.
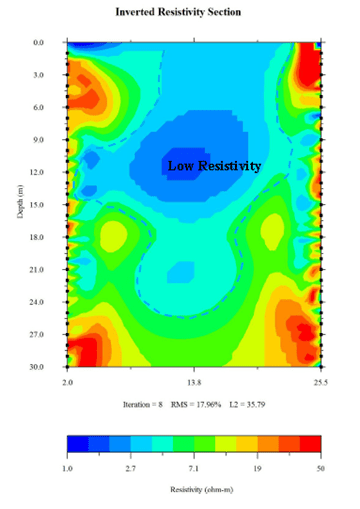
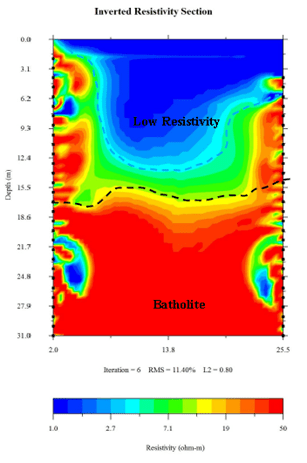
According to the present profile data:
- The low resistivity layer on the surface layer from 0 to 1 meter, with a value of 1 – 5 ohm – m, is caused by surface water infiltration.
- Below 1 meter in depth, the low resistivity of water is caused by cracks.
- Near the surface, the local high resistivity in the line is led by the artificial cement in the surface layer. At a depth of 15 meters, the high resistivity value of 16 ohm – m is deduced to be related to rock.
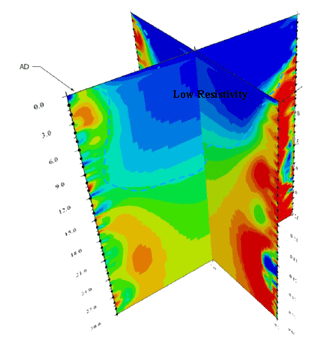
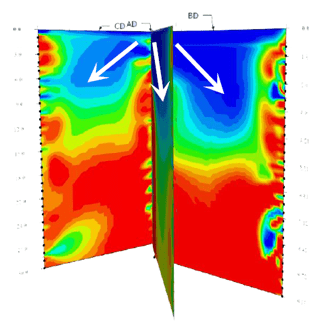
As a result, in the directions of A→D, B→D, and C→D:
- Both the C hole and D hole are in lower resistivity areas.
- The trend of low resistivity extends continuously from the C hole and D hole towards A and B.
It is confirmed that:
- The middle zone of the 4 holes is a low resistivity block. It may be a temporary water layer caused by the original temporary water layer or fissure.
- The A→D and B→C lines can confirm that the middle zone of the well is a low resistivity area.





For more information about Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) principles, please refer to the following article for more information.https://geotechcn.net/service/geophysical-methods-a-comprehensive-guide-to-electrical-resistivity-tomography-ert/
FAQ
The double tap has a large current and can be used for IP testing to get more accurate data.
High-density apparent resistivity method is an array prospecting method, also known as automatic apparent resistivity system, which is developed from direct current method. Its function is equivalent to the combination of quadrupole sounding and electrical profiling method. The artificial electric field is formed by supplying electricity to the underground through electrodes. The distribution of the electric field is closely related to the distribution of the resistivity of the underground rock and soil medium. By measuring the artificial electric field at different parts of the surface, the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the underground medium is understood, and the underground geological structure is inferred and interpreted based on the distribution of the apparent resistivity of the rock and soil medium.
The principle of high-density electrical method is the same as that of traditional resistivity method. It is a combination method of multiple devices and multiple pole distances that integrates electrical depth sounding and electrical profiling method, which can obtain the conductivity characteristics of two-dimensional underground media. It has the characteristics of multi-device data acquisition in one pole arrangement, and highlighting abnormal information by obtaining ratio parameters, which greatly increases the amount of collected data, improves work efficiency, and ensures the accuracy and reliability of the pole running process.
This method is particularly sensitive to the water content of the surrounding rock. If the surrounding rock is broken and contains water, its apparent resistivity is significantly reduced. The apparent resistivity of intact and hard rock and soil is significantly higher than that of the surrounding rock in the fault zone or broken zone and water-rich zone. This method has a clear principle and intuitive images. It is a geophysical method with high resolution. In recent years, with the improvement of computer data acquisition technology, the exploration efficiency has been greatly improved, the coverage area and detection depth of the profile have been increased, reliable data can be obtained in a strong interference environment, the signal-to-noise ratio has been greatly improved, and the geological body can be accurately detected. This method has been widely and successfully applied in engineering and hydrogeological exploration and exploration of mineral and water resources.
(1) Application in coalfield and mine goaf detection
(2) Non-destructive detection of termite nests in dam foundations
(3) Karst and foundation surveys of railways, roads and tunnels
(4) Delineation of stratum lithology boundaries
(5) Survey of the leakage range of landfills
(6) Ancient tomb surveys
(7) Detection of sewage pipes
(8) Non-destructive testing of leakage in reservoirs and river dams
(9) Detection of bedrock fracture zones
(10) Soil salinity and water quality surveys
(11) Detection of ancient tunnels, air-raid shelters, metal burial sites, etc.
(1)The high-density resistivity method is based on the resistivity method, so it is suitable for all underground explorations with obvious conductivity differences;
(2)Any medium underground will have a weak polarization potential at the moment of power on and off, which will affect our measurement of the true potential difference. When the electrode distance is small, the loop current is large, which has little effect on the measurement results; when the electrode distance is too large, the interference potential is close to the effective potential, which has a greater impact on the measurement results. Therefore, due to the influence of the power supply electrode distance, the exploration depth cannot be too large, generally within 100m. When the conductivity of the soil medium is good, it can be appropriately increased, and the exploration depth in the soil medium with poor conductivity is appropriately smaller;
(3)It is generally less used in cities, near large transmission lines, etc. due to site restrictions and industrial stray current interference; 4. In areas such as concrete pavements and exposed bedrock surfaces, it is also less used due to the difficulty of electrode layout.
-1.png)






